Your Complete Guide to Game-Based Learning and Its Scope in Education
Game-based learning, as the name suggests, is gameplay with defined learning goals, and designed to present subject matter in the form of a game to help learners understand the concepts. Often in a simulated environment and gain experience with their applications in a virtual environment before using them in the real world.
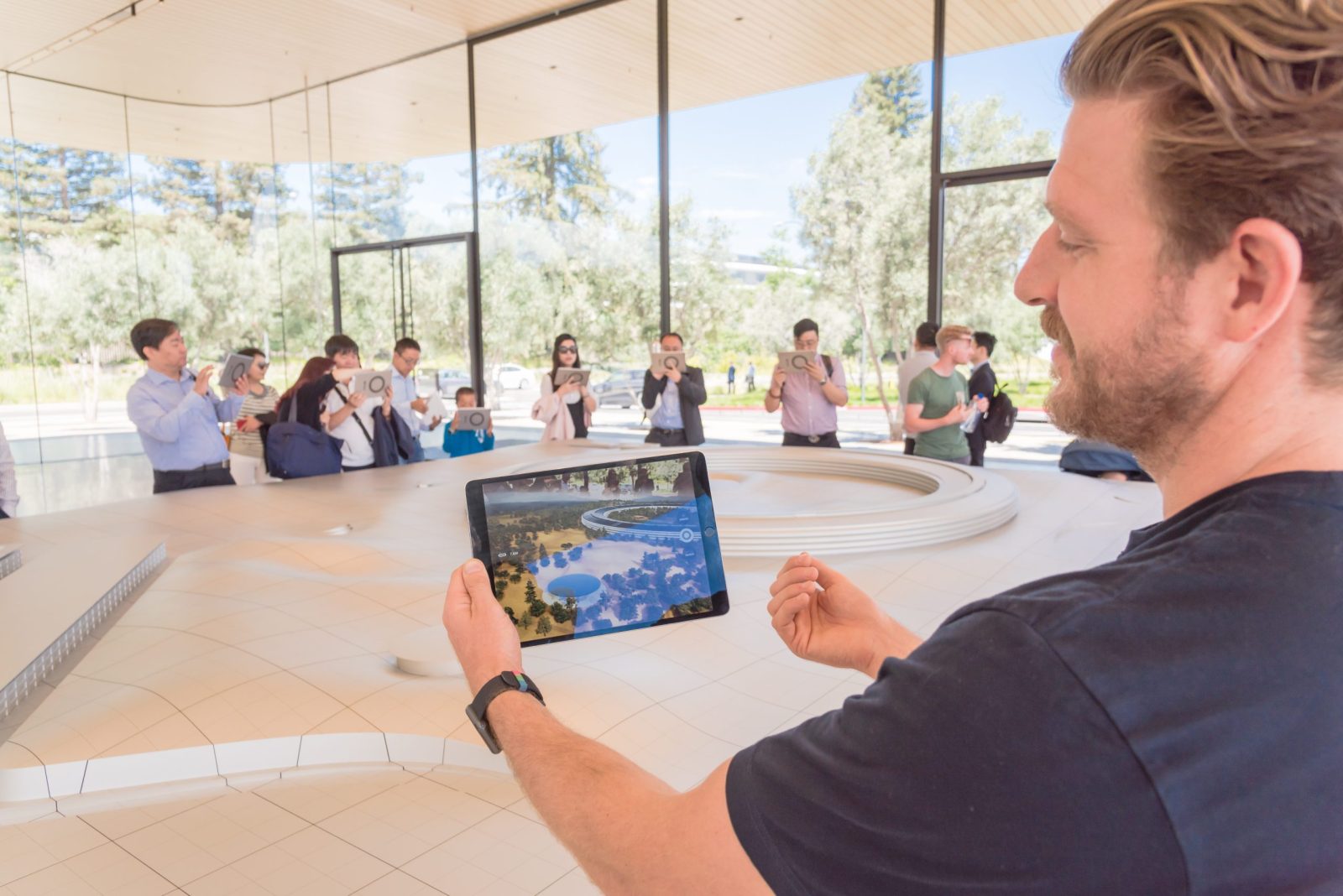
Game-based learning can take place in a virtual environment or a simulated environment created by augmented reality. Virtual environments resemble real-life settings while augmented reality goes one step further by presenting an enhanced version of reality. Unlike virtual reality, AR does not create a virtual environment, rather it imposes a 3-D dimension or 360-degree view to the environment using computer-generated information to create an enhanced version of the existing reality.
Table of Contents:
- What is Game-Based Learning?
- What is Gamification in Education?
- How Game-Based Learning Enhances Learning Outcomes
- How to Design Effective Game-Based Learning Solutions?
- How to Measure the Success of Game-Based Learning for Your Students?
- What are the 4Cs of Game-Based Learning?
- Critical Thinking
- Creativity
- Communication
- Collaboration
- Game-Based Learning Method Helps Cultivating Skills for Life
- Unique Ways for Game-Based Learning
- Benefits of Game-Based Learning
- Is Game-Based Education Here to Stay?
- In Conclusion
What is Game-Based Learning?
Game-based learning is a type of learning that integrates the use of games to provide a more engaging, immersive, and effective learning experience. It involves the application of gaming elements and principles in learning environments.
The goal is to enhance the motivation, engagement, and overall learning process of the students or participants. In game-based learning, the learners are put into a game scenario where they need to achieve certain objectives or goals. These goals align with the learning objectives of the course or training program.
As the learners navigate through the game, they acquire new knowledge and skills, apply what they have learned, solve problems, make decisions, and receive feedback on their performance.
Game-based learning can take various forms, including video games, board games, card games, digital games, simulations, virtual reality & augmented reality. It can be used in various settings, such as classrooms, workplaces, online courses, and training programs.
What is Gamification in Education?
Gamification in education is the application of game elements into a non-game context. In other words, educators may create games as part of oral instruction, written instruction, etc. Games are not the primary instructional tool. Instead, they are one tool educators use to challenge, motivate, and inspire students.
Examples of gamification in learning include:
- Timed challenges
- Timed tests
- Classroom leaderboards
- Points and award-based incentives (stickers, badges, etc.)
- Judged contests, debates
- Competitive challenges (spelling bee, geography bee, etc.)
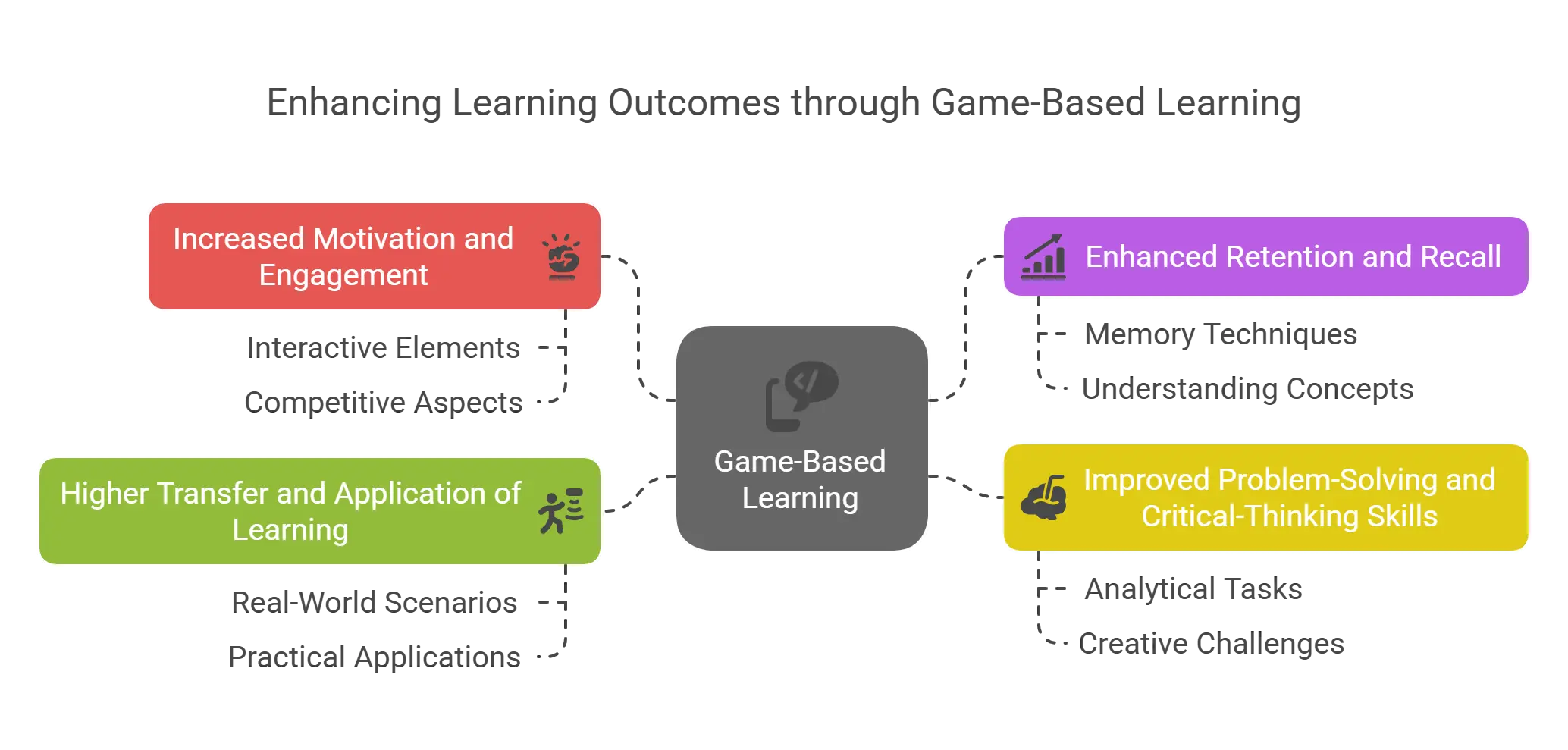
How Game-Based Learning Enhances Learning Outcomes
Game-based learning can offer many advantages for learners and educators, such as:
1. Increased Motivation and Engagement
Games can capture the attention and interest of learners, making them more willing to participate and learn. They can also provide rewards and recognition, which can boost learners’ confidence and satisfaction.
2. Enhanced Retention and Recall
Playing games can help learners remember and apply what they have learned, as they can reinforce learning through repetition, practice, and feedback. They can also create memorable and emotional experiences, which can improve learners’ recall and retention.
3. Improved Problem-Solving and Critical-Thinking Skills
As games can present complex and realistic scenarios that require learners to make decisions and solve problems, they can challenge learners to think creatively, analytically, and strategically.
In fact, according to a study published in the International Journal of Technology in Education, the application of game-based learning in education has contributed to a 67% increase in student achievement in problem-solving.
4. Higher Transfer and Application of Learning
Because games simulate authentic and relevant contexts and tasks that learners may encounter in lives, they can help learners transfer and apply their learning to real-world situations.
In addition to providing immediate and constructive feedback, games can assist learners in improving their performance and learning from mistakes, thereby enabling them to improve their performance.
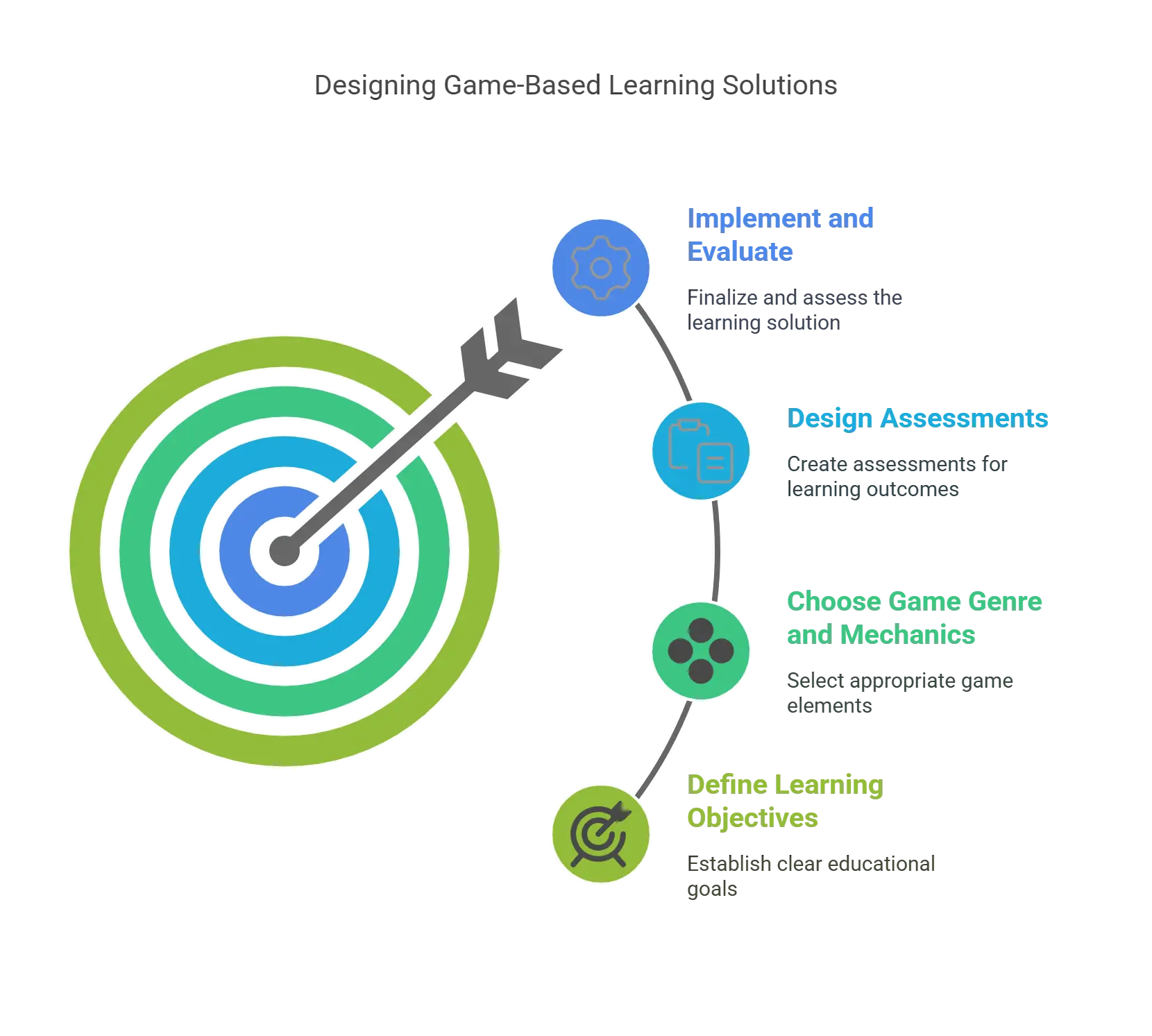
How to Design Effective Game-Based Learning Solutions?
To create engaging and impactful game-based learning solutions, you need to follow some key steps, such as:
1. Define Your Learning Objectives and Outcomes
Before you start designing your game, you need to identify what you want your learners to achieve and how you will measure their success.
You need to align your game with your learning objectives and outcomes and ensure that your game is relevant and meaningful for your learners.
2. Choose the Right Game Genre and Mechanics
Depending on your learning objectives and outcomes, you need to select the most suitable game genre and mechanics for your game. For example, you can use adventure games, simulation games, puzzle games, role-playing games, etc.
You also need to consider the game elements that will make your game engaging and fun, such as story, characters, graphics, sound, levels, challenges, rewards, etc.
3. Design the Game-Based Learning Assessments
To evaluate the effectiveness of your game-based learning solution, you need to design game-based learning assessments that will test your learners’ knowledge, skills, and abilities.
You need to ensure that your assessments are aligned with your learning objectives and outcomes and that they provide meaningful and actionable feedback to your learners. Use various types of assessments, such as quizzes, scenarios, simulations, etc.
4. Implement and Evaluate Your Game-Based Learning Solution
Once you have designed your game-based learning solution, you need to implement it and test it with your learners.
You need to collect and analyze the data and feedback from your learners and measure the impact of your game-based learning solution on their learning outcomes. Don’t forget to review and improve your game-based learning solution based on the results and feedback.
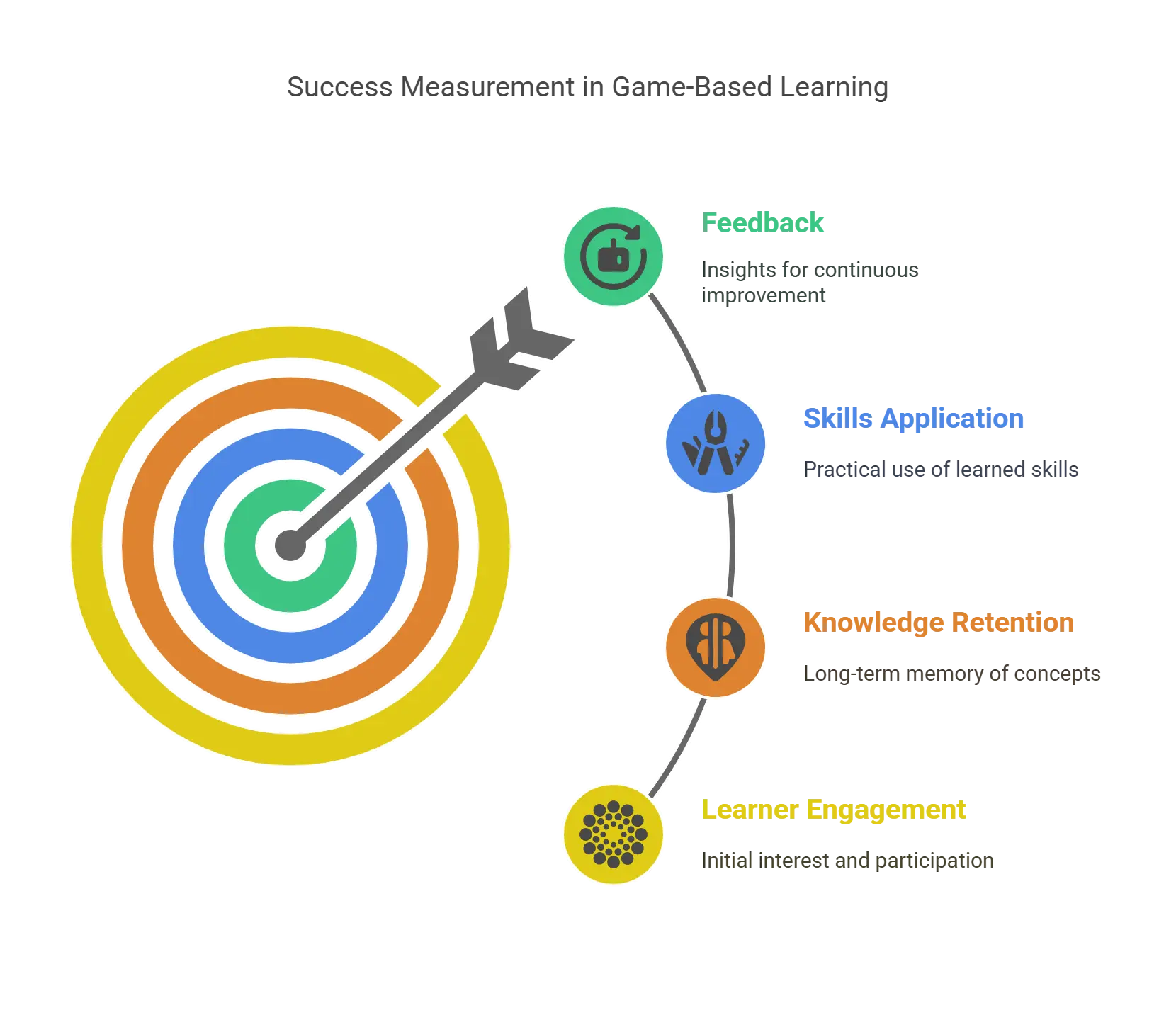
How to Measure the Success of Game-Based Learning for Your Students?
Measuring the success of game-based learning is crucial to ensure that your team is benefiting from the training. Here are some ways you can measure the success of your game-based learning:
1. Learner Engagement
Engagement is a key indicator of the success of any learning program, and game-based learning is no exception. You can measure engagement by tracking metrics such as the number of times learners log into the game, the amount of time they spend playing, and the number of levels or challenges they complete.
High engagement levels suggest that learners find the game interesting and are motivated to learn. You can also look at the progress learners make in the game, as this can indicate how well they are grasping the material.
2. Knowledge Retention
To measure knowledge retention, you can conduct assessments or quizzes after the game-based training. These assessments should be designed to test the knowledge and skills that the game was intended to teach.
If learners perform well on these assessments, it suggests that the game-based learning experience was effective in helping them retain the information.
3. Skills Application
Observing if your team is applying the skills and knowledge gained from the game in their work is a crucial measure of success. This could be measured through performance reviews or feedback from supervisors.
4. Feedback
Gather feedback and ask learners about their overall experience with the game, what they liked and disliked, and any suggestions they have for improvement. This feedback can help you understand the learners’ perspective and make necessary adjustments to enhance the learning experience.
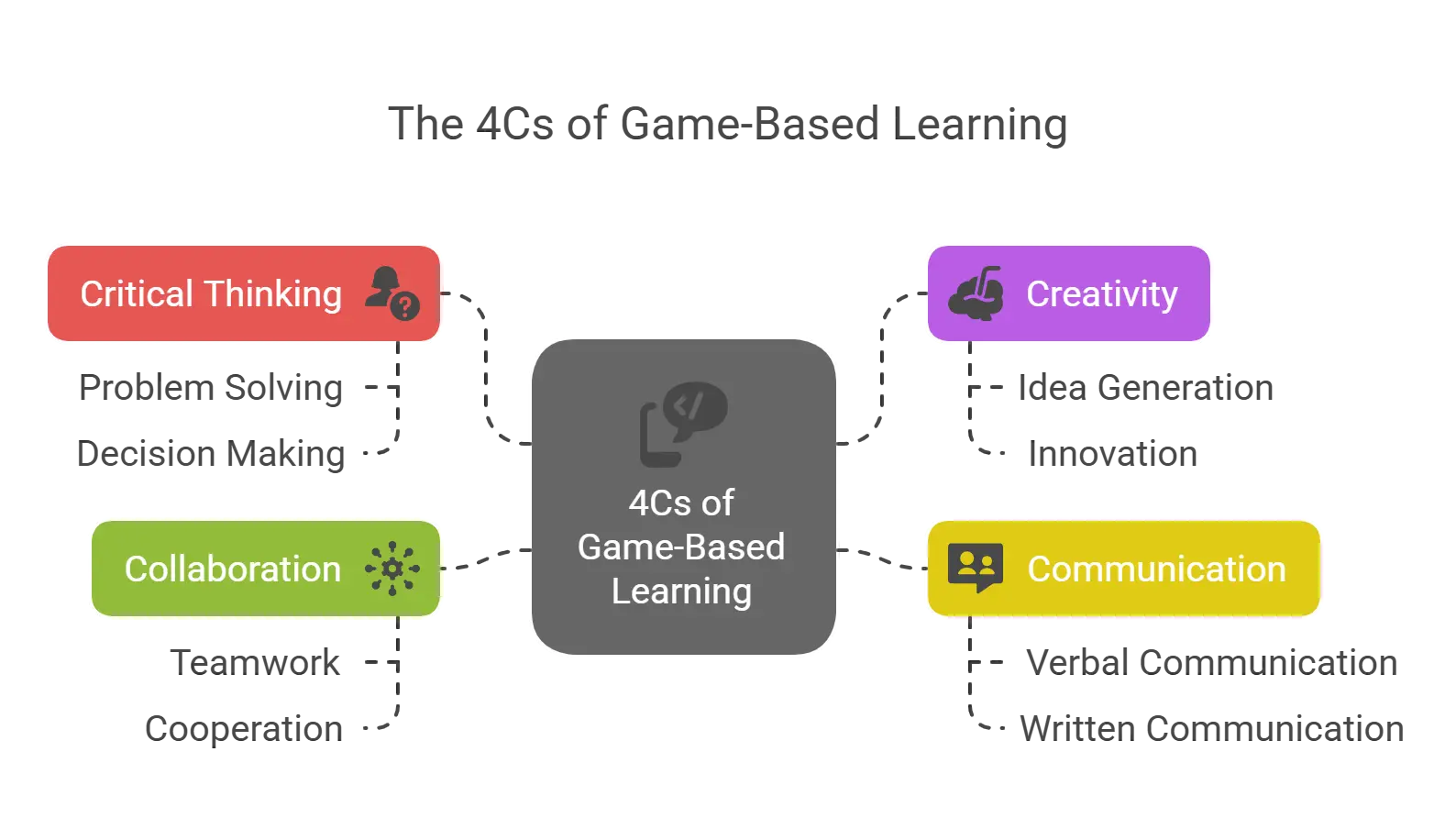
What are the 4Cs of Game-Based Learning?
There are 4 important pillars that build an effective game-based learning strategy. Here are the 4 Cs:
1. Critical Thinking
Experts agree that the development of critical thinking skills is essential in K12 education. Some argue that it is the most important skill for students to learn. Defined as “the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue to form a judgment,” critical thinking may also be summarized as being able to make reasoned judgments, which are logical. Others may view critical thinking as the ability to decide what is true, and what you should therefore do.
Irrespective of how you would personally define it, all critical thinking requires decision-making and careful analysis. Considering that digital learning games require players to make decisions after decisions while playing them, it follows that online game-based learning helps to foster critical thinking skills.
Critical thinking skills will be required as students progress through their education, and into the workforce. As a highly transferable skill, students must learn how to think critically when young, and continue to practice the skill as they age. With digital learning games available for all K12 levels, the game-based learning method is an incredibly useful tool for educators worldwide.
2. Creativity
The world’s foremost innovators are unabashedly creative individuals. Why? Because creativity leads to innovation. Were the world’s most successful entrepreneurs and innovators born this way? Perhaps. But creativity can also be taught, and digital learning games can be an excellent tool for teaching students to think outside the proverbial box.
But how exactly does the game-based learning method foster creativity?
A. Problem-Solving Challenges
Solving problems to advance to the next level in digital learning games requires students to formulate strategies for solving puzzles, riddles, and even in-game tricks. It leads to the development of innovative solutions.
Consider, for example, games that allow players to build their cities. They will be tasked with feeding the civilizations, meaning they must grow or hunt food. But, they determine the best tools and weapons to create the food. They will have to solve the problem of shelter or housing, which requires careful consideration of the materials and resources available.
In all high-quality educational video games, players will have to solve a multitude of problems ranging from simple to complex.
B. Immersive, Artistic Experiences
Game-based learning methods intentionally expose students to vibrant colors, imaginary worlds, music or sounds, and augmented reality of storytelling, which in and of themselves are creative. Games are so effective at introducing students to creative expression, that studies have shown that children who play video games were more creative in their drawings and storytelling than those who played fewer video games.
C. Personalization
Many online game-based learning tools available from top K12 education companies allow the players to personalize their character, their world, or their narratives. From designing an avatar to creating a working farm, to crafting a personal narrative through choices made, the ability to create directly within the game can help promote creativity.
3. Communication
Communication is the third C of game-based learning. Game-based learning methods support communication skill-building in a variety of ways. Firstly, students will need to communicate with their peers if playing digital learning games as a team. They may also need to communicate effectively with the game via in-game chats, voice chats, or even online forums.
In post-gameplay classroom discussions, students further hone their communication skills by explaining what their strategy was for advancing to the next level. They may learn to debate the merits of one choice compared to another choice. They will gain meaningful practice in clearly and persuasively communicating with others.
Moreover, game-based learning can support non-verbal communication skills. For example, clues given in games, or gestures of characters in games help students to develop a broad set of communication skills that will serve them as they matriculate into college, and ultimately enter the workforce.
4. Collaboration
The final pillar of the four Cs of game-based education is collaboration. Collaboration is championed through the game-based learning method. Digital learning games require students to partner with others in team events. They may require compromising with other players to ensure that all students get equal play time. Players may need to build partnerships or learn to barter with one another in other digital learning games. Collaboration helps to cultivate critical skills including empathy, teamwork, and leadership, all of which are essential to succeeding in the 21st Century.
Game-Based Learning Method Helps Cultivating Skills for Life
At the heart of the game-based learning method are the Four Cs: Collaboration, Communication, Critical Thinking, and Creativity. These four pillars form a foundation for successful game-based education. These skills are invaluable in K12 education and necessary for success in higher education or the workforce.
Even better? Online game-based learning offers immersive and interactive environments where students have fun while developing these critical skills. As such, educators who wish to increase student engagement, motivation, knowledge retention, and digital literacy can rely on game-based learning products from top K12 education companies to deliver the games that will accomplish these objectives.
Unique Ways for Game-Based Learning
There is a reason why games have a short popularity lifespan. Barring evergreen titles like COD and CS:GO, most games fail to maintain relevance.
The same will happen if you only introduce a handful of games and related activities. Try rotating between group games, whole-class games, and solo activities to keep the learning experience fresh.
1. Story-Based Learning
A story-based narrative can help you create an interactive and compelling storyline-based game to engage the students.
For example, you can introduce a situation where students have become part of an environmental organization trying to preserve an ecosystem. Add issues such as habitat destruction, pollution, and deforestation. Students will be needed to make choices to preserve the habitat. This makes the session interesting while eliminating any safety concerns.
2. Escape Room Sessions
You can design escape room-like activities where students must find and implement relevant clues to progress. The approach will simulate their critical thinking and hone their collaborative skills while helping them make deductions on the go.
Since 97% of learners desire to play and perform activities, a mystery activity session can delight them.
3. Interactive Online Challenges
Game-based assessment and learning can also be conducted online. You can create interactive puzzles and quizzes that deliver instant feedback.
Based on the instant results, learners can track their progress, retake the quizzes, and compete with others. It will reinforce their learning while making the session engaging.
4. Role-Playing Simulations
You can also leverage role-playing simulations to help learners immerse themselves in the topics to increase their retention. For example, students can imitate historical figures instead of giving them lengthy texts to read about their lives. The sense of immersion will help students deeply comprehend the situation.
Given the prevalent use of technology in day-to-day activities, using it to teach can be highly beneficial. Let’s see how:
Benefits of Game-Based Learning
1. Gen Z’s Familiarity with Technology
Gen Zers enjoy interacting through technology and are incredibly adept at using it, always looking for innovative ways to learn. That is why 59% use YouTube and 47% play interactive games to increase their skills. Thus, using online game-based learning to make their education more engaging can be highly beneficial.
2. Simulating the Imagination
Game-based teaching equips students with tools like 3D models to deploy in real time. This can help them better understand the topic, making the experience more real and enjoyable.
A digitally created world where learners can interact with elements can simulate their imagination. It can make a lasting impression, helping them associate the information with the experience and increasing knowledge retention.
3. Improved Motivation
Students who experience a gamified learning approach have enjoyed the process. They reported that the approach reinforced their knowledge, helping them engage and communicate with fellow students.
Thus, using gaming technology in interactive learning can lead to better student motivation.
4. Better Knowledge Retention
Using interactive videos is also a good idea for an improved learning experience. Students only retain 10% to 20% of the knowledge they have read or heard after three days.
However, their knowledge retention increases significantly when videos and illustrations are involved. Thus, teachers can use such interactive elements to elevate learners’ knowledge retention.
5. Learning Practically
Game-based learning can boost your existing interactive learning strategies by adding teamwork. For example, teachers can hold an interactive session to explain the concept of projectile motion. A game can allow students to try different scenarios to understand trajectory, height gained, distance traveled, etc.
Turning the session into a competition using blending and segmenting activities will also motivate them to collaborate. Participatory activities can help students retain knowledge about complex concepts. Thus, using blended learning can help learners collaborate while retaining more knowledge.
Is Game-Based Education Here to Stay?
By all indications, gamified learning, specifically through the use of game-based learning solutions, will play a significant role in the future of education. As technology advances at the fastest pace in human history, educators are likely to embrace game-based e-learning, to ensure students are equipped for a highly digitized world beyond primary and secondary education.
In addition to offering an engaging learning experience, the data-driven insights educators can glean in just seconds are unmatched by traditional methods. Educators can immediately identify students who are struggling, and students who are not being challenged enough. Moreover, adding educational technology to the repertoire of tools educators rely on, may reach students who struggle to engage with learning via traditional educational approaches. However, it is unlikely that game-based learning will replace traditional instruction for students in the foreseeable future.
In Conclusion
Game-based learning can be highly beneficial, especially among Gen Zs and young learners. Seeing how most learners are familiar with games and technology, using GBL can boost their learning experience. Moreover, it can help them retain knowledge.
With Hurix Digital’s learning management, you can integrate intuitive and appealing strategies into your traditional teaching regime. The platform has a comprehensive eLearning and training solution to gamify your learning experience.
You can reach Hurix Digital today and boost your teaching sessions with the power of gaming.

Senior Vice President – Business Development
at Hurix Digital, with over 25 years of experience in EdTech and workforce learning. He excels in business development, customer relationship management, and scaling digital learning solutions, driving global growth through innovative content, simulations, and AI‑driven training offerings








