
5 Popular Curriculum Development Models You Should Know
Summarize with:
The curriculum is fundamental to guiding formal learning, tailored to each institution’s educational goals. Curriculum development models guide the design and development, ensuring courses align with learning objectives and institutional philosophy. These models help create effective and relevant educational experiences. Curriculum development models serve as a guide for two important processes involved in curriculum creation: design and development.
Broadly defined, curriculum design refers to a course’s overall structure or blueprint. Meanwhile, curriculum development is a step-by-step procedure that involves planning, implementing, evaluating, and improving course materials and teaching strategies to produce better educational outcomes.
As an educator, being aware of the different curriculum development models will enable you to make informed decisions and chalk out an effective learning plan for your institution.
So, let’s dive in!
Table of Contents:
- What is a Curriculum Development Model?
- What are the 5 Types of Curriculum Design Model?
- Tyler’s Curriculum Model (Best for Outcome-Driven Learning)
- Taba’s Grassroots Model (Teacher-Led Curriculum Design)
- John Goodlad’s Curriculum Model (Best for Holistic and Value-Oriented Curriculum Design)
- Wheeler’s Curriculum Model (Approach to Cyclical Curriculum Development)
- Kerr’s Curriculum Model (Focus on Systematic and Balanced Curriculum Planning)
- Side-by-Side Comparison of Curriculum Development Models
- How Educators Apply These Models in Real Classrooms?
- The Bottom Line: Choosing the Right Curriculum Development Model
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Curriculum Development Model?
A curriculum development model is a structured framework used to plan, design, implement, and evaluate educational programs. It helps educators systematically define learning objectives, select relevant content, choose effective teaching strategies, and assess learner outcomes to ensure educational goals are met.
These models guide key curriculum decisions by answering essential questions such as what students should learn, how learning should be delivered, and how success should be measured. By following a clear sequence or cycle, curriculum development models bring consistency, clarity, and quality to instructional planning.
Curriculum development models are used across K–12 education, higher education, corporate training, and digital learning environments. Some models focus on outcome-based planning and assessment, while others emphasize teacher involvement, learner needs, or continuous improvement. Selecting the right model depends on factors like learner profiles, subject complexity, and institutional objectives.
Understanding curriculum development models enables educators and instructional designers to create effective, learner-centered, and adaptable curricula.
What are the 5 Types of Curriculum Design Model?
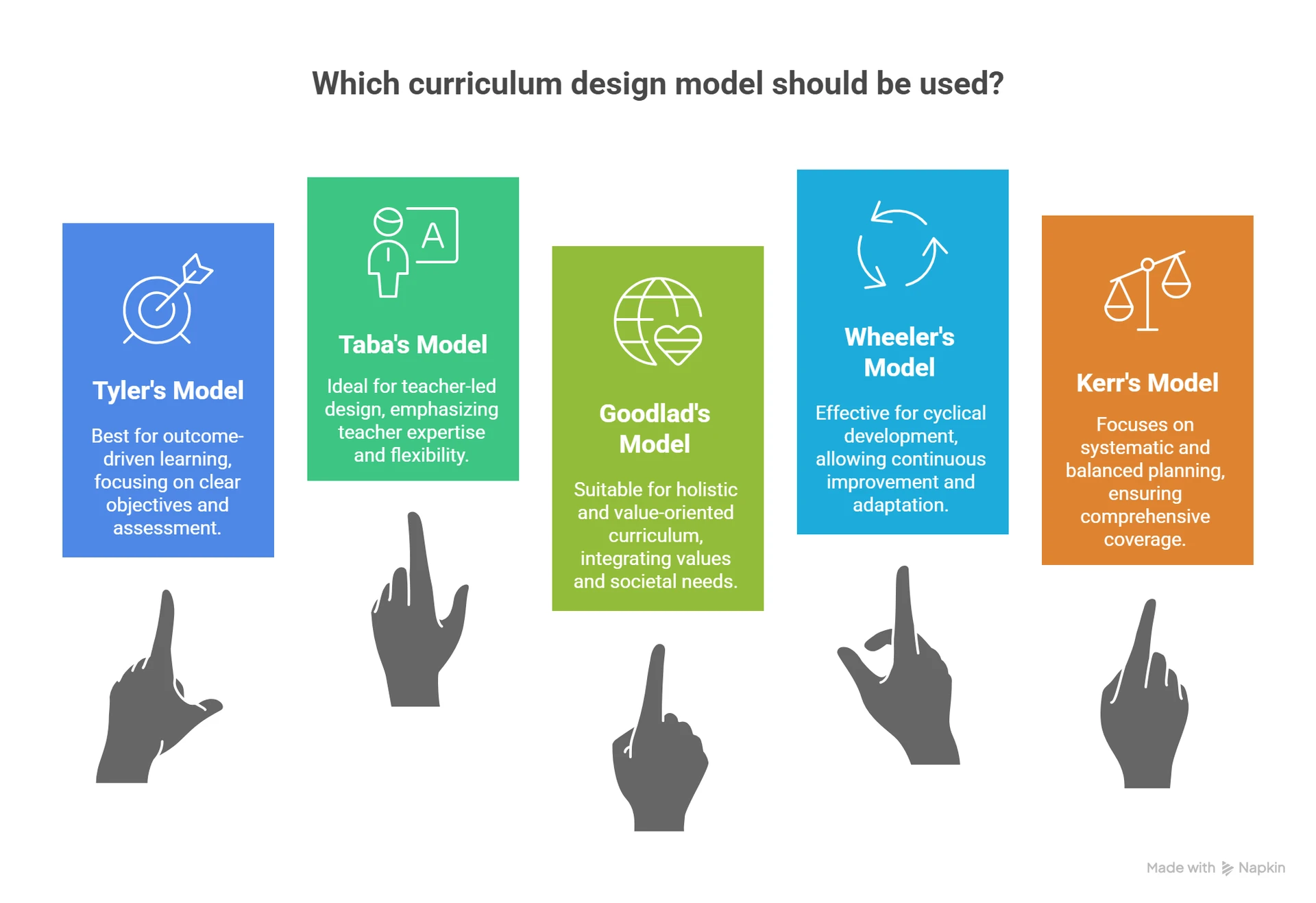
There are several models for developing a curriculum. Here are a few popular ones:
1. Tyler’s Curriculum Model (Best for Outcome-Driven Learning)
Tyler’s Model was developed by American educator Ralph W. Tyler in 1949. It is also known as the objective Model and is among the most widely used curriculum design models. It is based on the notion that the objective of education is to develop learning that is meaningful and useful to learners.
Tyler’s Model lays importance on the planning phase. At the same time, it focuses on maintaining consistency among objectives, outcomes, and educational experiences. It is a linear model that considers four fundamental aspects of developing a curriculum, including:
- The purpose or objective of education to be achieved
- The learning experience required to attain the defined objective
- Organizing educational activities for effective learning experiences
- Assessing the Learning experiences
The strength of this Model lies in its concise structure and systematic approach. At the same time, it allows for flexibility. Educators can easily apply this Model to develop curriculum for any level of education and subject area.
Since it gives importance to the evaluation of the curriculum, Tyler’s Model enables educators to assess the effectiveness of their educational plans and introduce required changes.
However, Tyler’s Model has limitations. It gives less importance to social learning and doesn’t fully address critical thinking or emotional development. Consequently, this model might not comprehensively meet the diverse needs of all students. How can educators supplement Tyler’s Model to address these gaps?
2. Taba’s Grassroots Model (Teacher-Led Curriculum Design)
Taba’s Model, also known as the interactive Model, emphasizes the planning of instructional strategies. Designed in 1962 by Hilda Taba, an Estonian-American curriculum expert, reformer, and teacher, this model focuses on a dynamic, responsive approach to curriculum development. What are the key benefits of using an interactive model in curriculum design?
It follows a Grassroots or Down-Top approach and promotes a major role for teachers. The Model consists of seven stages of the learning and teaching system, which are mutually interactive.
They are as follows:
- Diagnosis of learners’ needs
- Formulation of objectives
- Selection of the content
- Organization of the content
- Selection of learning experiences
- Organization of learning activities
- Evaluation
This Model promotes open-ended questions rather than focusing on right or wrong responses. One of the major benefits is that it offers scope to explore a concept at a deeper level using critical thinking skills.
3. John Goodlad’s Curriculum Model (Best for Holistic and Value-Oriented Curriculum Design)
A Canadian theorist and educational researcher, John Goodlad, conceptualized Goodlad’s Model. It is a distinctive curriculum based upon the core belief that the driving force of educational systems should be values or goals. Goodlad considered values as data sources, contrasting Tyler’s consideration of values as a screen.
In his curriculum development model, Goodlad focuses on four key data sources:
- Values
- Funded knowledge
- Conventional wisdom
- The learner’s needs and interests
These sources differ significantly from Tyler’s Model. How does Goodlad’s emphasis on values as data sources impact curriculum design?
One of the major differences is that Goodlad’s Model recognizes scientific knowledge that stems from research. When it comes to data sources, the Model depends on explicit value statements. This Model proposes continuous evaluation at all stages of the curriculum development process.
Also Read: Curriculum Design: How To Develop A Successful Curriculum
4. Wheeler’s Curriculum Model (Approach to Cyclical Curriculum Development)
Wheeler’s Model, devised by British educator and researcher D. K. Wheeler, is cyclic. This Model uses a systematic and structured process to design and implement a curriculum, ensuring continuous improvement and adaptation. What makes a cyclic model beneficial for curriculum development?
It aims to help educators create and implement a dynamic curriculum that is relevant, effective, and efficient. Wheeler’s Model comprises five phases of curriculum development, which are as follows:
- Selection of aims, goals, and objectives
- Selection of learning experiences
- Selection of content or subject matter
- Organization and integration of learning experiences and content
- Evaluation and revision of curriculum
Wheeler developed this Model to address the shortcomings of Tyler’s concept of curriculum development. Since Tyler’s Model is linear and basic, it overlooks the relationship between different curriculum elements. In response to it, Wheeler proposed this cyclic Model.
It underlines the interconnectedness of the various curriculum aspects. This Model enables curriculum designers to begin working on it at any stage. It also focuses on situational analysis. However, this Model is time-consuming and may be difficult to implement.
5. Kerr’s Curriculum Model (Focus on Systematic and Balanced Curriculum Planning)
Proposed by British curriculum specialist John Kerr, Kerr’s Model of curriculum development shares features with Tyler’s and Wheeler’s Models. However, it uniquely emphasizes the interrelatedness of its components through direct and indirect data flow. How does this emphasis on interrelatedness improve curriculum design?
John Kerr proposed four components for his curriculum development model:
- Objectives
- Knowledge
- School learning experiences
- Evaluation
Kerr’s Model recommends sorting objectives as cognitive, psychomotor, and effective. It also underlines that knowledge needs to be organized, integrated, sequenced, and reinforced.
This Model pays attention to the needs and interests of students, the influence of social conditions and school, and the maturity of the learners. However, one drawback is that it doesn’t focus on teacher input.
Side-by-Side Comparison of Curriculum Development Models
| Curriculum Development Model | Core Focus | Key Characteristics | Best For | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tyler’s Curriculum Model | Learning objectives and outcomes | Linear, objective-driven, assessment-focused | Outcome-based education, standardized curricula | Limited flexibility; less learner input |
| Taba’s Grassroots Model | Teacher-led curriculum design | Inductive approach, bottom-up planning, flexible | Classroom-level curriculum design | Time-intensive; harder to scale |
| John Goodlad’s Model | Holistic curriculum development | Emphasizes values, social goals, and learner needs | Broad educational reform and value-based education | Less structured; complex implementation |
| Wheeler’s Curriculum Model | Continuous curriculum improvement | Cyclical process, ongoing evaluation and revision | Dynamic learning environments | Requires constant review and resources |
| Kerr’s Curriculum Model | Balanced curriculum planning | Interconnected objectives, content, learning, evaluation | Systematic and integrated curriculum design | Can be complex for small institutions |
How Educators Apply These Models in Real Classrooms?
Directors of Educational Program Development can leverage curriculum development models to enhance their programs in the following ways:
1. Structure the Curriculum Development Process
You can follow the structured approach provided by these models to guide the entire curriculum development process from start to finish. You can implement step-by-step processes to ensure thorough planning and execution.
2. Enhance Stakeholder Involvement
These models facilitate the involvement of teachers, students, and parents in curriculum development, fostering collaboration among content creators, curriculum developers, publishers, and educators to create a cohesive and effective learning experience. Why is stakeholder involvement crucial for successful curriculum development?
3. Improve Learning Experiences
You can select relevant and engaging content and devise innovative learning experiences that are customized according to different learning preferences. Additionally, you can incorporate diverse teaching strategies and promote critical thinking to create a dynamic and effective educational environment that supports student success and fosters lifelong learning.
4. Professional Development
You can provide industry-related knowledge and professional development opportunities for educators to understand and implement the curriculum. This way, you can ensure that educators are well-equipped to deliver the curriculum effectively and adapt to evolving educational practices.
5. Incorporate Technology
When it comes to integrating technology, you can use curriculum development models to guide the selection and implementation of digital tools and resources.
Here’s how:
- Identify objectives
- Select learning experiences
- Organize learning experiences
- Evaluate whether the objectives have been met using formative and summative assessments
- Provide training for teachers on designing assessments according to organizational objectives
- Conduct a diagnosis of needs
- Develop objectives, choose content, arrange it logically, and select appropriate learning activities to deliver the content
- Sequence learning activities effectively
- Assess the curriculum and make necessary revisions based on feedback
- You can establish the foundation of the curriculum, and create a broad framework by putting the designed curriculum into practice
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the curriculum and ensure it complements societal values
- Involve community members in the curriculum development process
- Design learning experiences based on objectives and make continuous improvements to the curriculum
- Create a curriculum that is flexible and adaptable
- Implement a feedback system for educators to refine the curriculum
- Define clear learning objectives and determine the knowledge that students need to acquire
- Design innovative learning experiences and measure the effectiveness of the learning experiences
This way, you can ensure that the curriculum is effectively structured, inclusive, engaging, and adaptable, ultimately enhancing the educational experience for students.
Also Read: What is Curriculum Development: Overview, Best Practices, and Future Trends
The Bottom Line: Choosing the Right Curriculum Development Model
Curriculum development is essential for all education programs, both online and offline. Designing and implementing an effective curriculum, especially for online learning, can be challenging. How can digital curriculum providers assist in creating successful educational programs?
Hurix Digital is one of the most reliable K12 curriculum development companies that designs customized curricula based on client requirements. The team of experts at Hurix Digital is adept at developing an eLearning curriculum and ensuring success for your educational programs.
Contact our expert team for all kinds of services related to digital curriculum development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Why are curriculum development models important?
Curriculum development models provide structure, consistency, and a systematic approach to curriculum planning, ensuring that educational objectives, content, and instructional strategies align with desired outcomes.
Q2: How do educators choose the most suitable curriculum development model?
Educators should consider educational goals, student needs, instructional approaches, and available resources when selecting a curriculum development model. Adapting and customizing models to fit specific contexts and learner characteristics is also important.
Q3: Can curriculum development models be used in various educational settings?
Yes, curriculum development models can be applied in different educational settings, including K-12 schools, colleges, universities, and vocational training institutions.
Q4: How can curriculum development models be tailored to specific subject areas?
Educators can customize curriculum development models by incorporating subject-specific content, skills, and pedagogical approaches that are relevant to the discipline being taught.
Q5: How can curriculum development models support educational innovation and improvement?
Curriculum development models provide a structured framework for incorporating innovative teaching practices, new technologies, and emerging educational trends into the curriculum to enhance learning experiences.
Q6: Do curriculum development models evolve?
Yes, curriculum development models evolve to reflect changes in educational theory, advancements in research, societal needs, and the evolving nature of knowledge and skills required for success.
Summarize with:

Senior Vice President – Business Development
at Hurix Digital, with over 25 years of experience in EdTech and workforce learning. He excels in business development, customer relationship management, and scaling digital learning solutions, driving global growth through innovative content, simulations, and AI‑driven training offerings
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 




