The Power of Accessible Solutions in Transforming Learning for All!
Summarize with:
The right to a quality education is a common aspiration among learners today. However, while universities have invested significant resources in this mission, many have fallen behind in serving one demographic: learners with disabilities.
As of 2023, the United States had over 7.2 million students with disabilities. Yet, despite the passage of a federal act in 1975, the Individuals With Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), students with disabilities applying to universities face challenges due to a lack of accessible infrastructure and an inclusive learning environment.
In this scenario, technology can be a game-changer. By adopting accessible solutions, colleges and universities can reduce barriers for learners with disabilities. As a result, they can attract this demographic of students, improve enrollments, and build an inclusive learning culture. Let’s understand what this process entails.
Table of Contents:
- What are Accessibility Solutions?
- Understanding Accessibility in EdTech
- The Role of Accessibility Consultants in Educational Publishing
- Why are Accessibility Audits Important?
- Challenges of Accessibility for EdTech Solutions
- Accessibility Tools and Technologies in Educational Publishing
- How to Conduct an Accessibility Audit?
- Steps to Implement Accessibility Solutions Effectively
- Final Words
What are Accessibility Solutions?
Today, accessibility software is helping to make many domains more accessible to people with disabilities—from travel and communications to healthcare and education. Educational institutions, for instance, can harness the power of accessibility software to build inclusive learning ecosystems.
By introducing accessible solutions and inclusive learning systems Institutions can attract more students with disabilities to enroll at the institute. They can also introduce online courses that can appeal to a larger demographic of students with disabilities across the world.
With the demand for accessible solutions growing, the market value of digital accessibility software is estimated to reach $ 0.75 billion in 2024 and $ 1.01 billion by 2029. Organizations that upgrade their ecosystems, products, and services to be accessible will, early on, have a competitive edge going forward.
Understanding Accessibility in EdTech
Like other websites and digital platforms, EdTech solutions must implement accessible solutions and adhere to digital accessibility requirements to ensure that all students can easily access and utilize the material.
This includes, but is not limited to:
- Visual Accessibility: Ensuring content is perceivable through alternative formats like screen readers and text-to-speech tools.
- Auditory Accessibility: Providing captions and transcripts for audio content.
- Motor Accessibility: Supporting keyboard navigation and ensuring interactive elements are operable without a mouse.
- Cognitive Accessibility: Designing interfaces that are clear, consistent, and easy to navigate.
The Role of Accessibility Consultants in Educational Publishing
Accessibility consultants play a great role in transforming educational publishing into an inclusive space. They bring the specialist perspective of accessibility laws, technology, and user needs to the creation of educational material and products. Their approach involves rigorous testing and content adaptation across multiple formats, from digital textbooks to interactive online platforms.
These consultants have a profound impact on educational content. They work closely with content creators to implement accessible solutions strategies that extend beyond compliance. These strategies involve using alt text for images, closed video captions, and improved digital interfaces to enable navigation through assistive technologies. These interventions aim to improve the usability and access of educational material for all, especially those with disabilities.
Furthermore, accessibility consultants advocate for universal design principles, ensuring that educational content benefits all students. This commitment to accessibility is increasingly recognized as essential in educational publishing, promoting broader engagement and more effective learning outcomes.
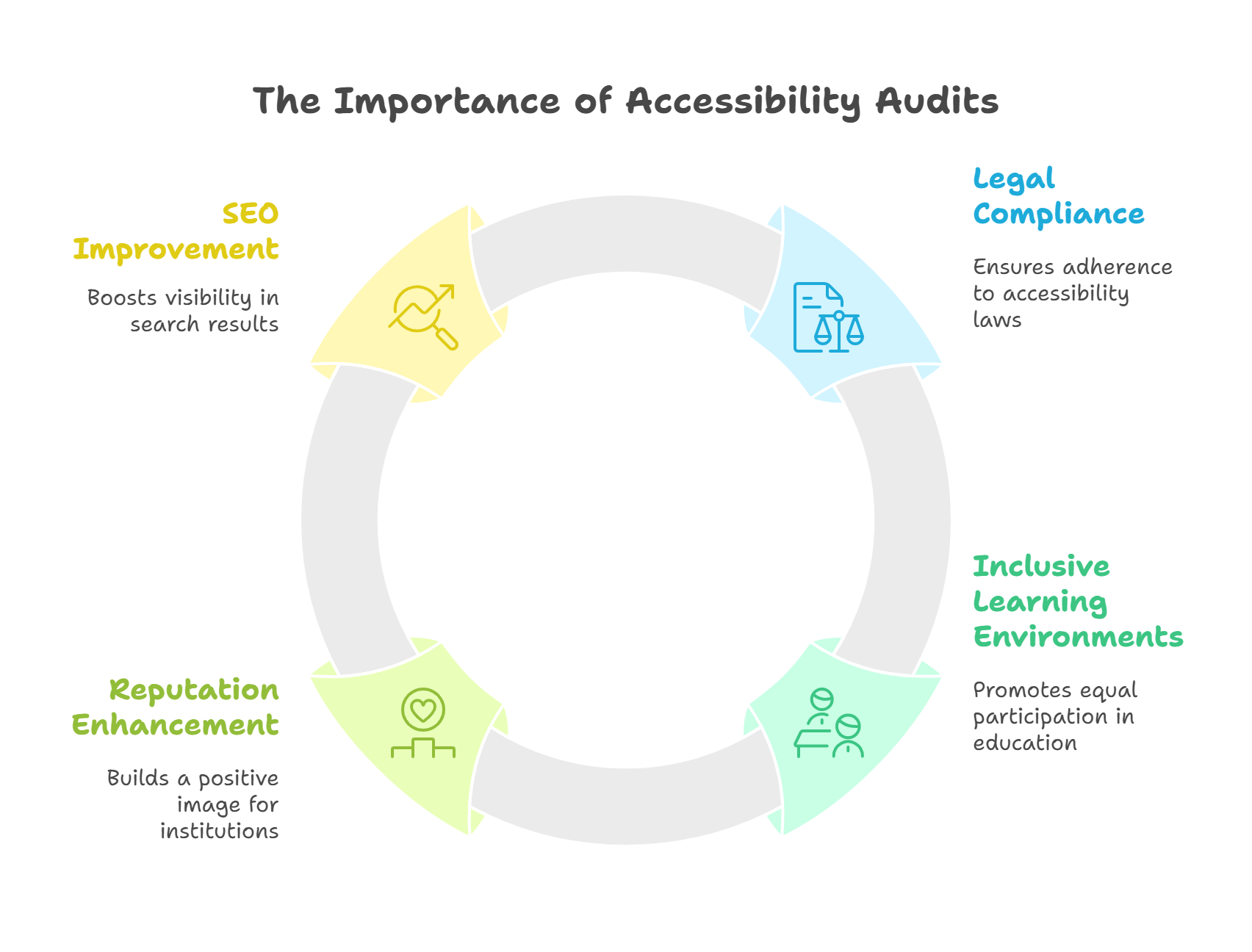
Why are Accessibility Audits Important?
Accessibility audits are crucial in ensuring digital accessibility and pinpointing areas needing improvement within educational technology.
1. Legal Compliance
Many nations have laws requiring digital products to be accessible by incorporating assistive technology and features.
For example, the Rehabilitation Act’s Section 508 and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) specify accessibility standards for federal services and programs, including those offered to US educational institutions that receive federal funding.
2. Creating Inclusive Learning Environments
Ensuring the user-friendliness of EdTech platforms facilitates equal participation in learning activities by students with varying abilities. This encourages the development of a more diverse learning environment where each student can succeed.
Additionally, accessibility audits allow teachers to identify areas for improvement and barriers to learning and create an inclusive learning space for all students.
3. Enhancing Reputation
Adhering to accessibility guidelines might seem easy, but it requires great effort and an advanced technological skillset.
Consequently, educational institutions and platforms that do regular accessibility testing and proactively work towards providing an inclusive learning environment to their students create a high reputation in the industry and attract a more diverse student body and teachers.
4. Improving Search Engine Optimization
Another positive aspect of conducting accessibility audits for EdTech solutions is improving SEO ranking.
Search engines automatically rank accessible websites and digital platforms higher than non-accessible ones. This dual benefit enhances usability and boosts visibility in search engine results, contributing to a more inclusive and widely accessible educational experience.
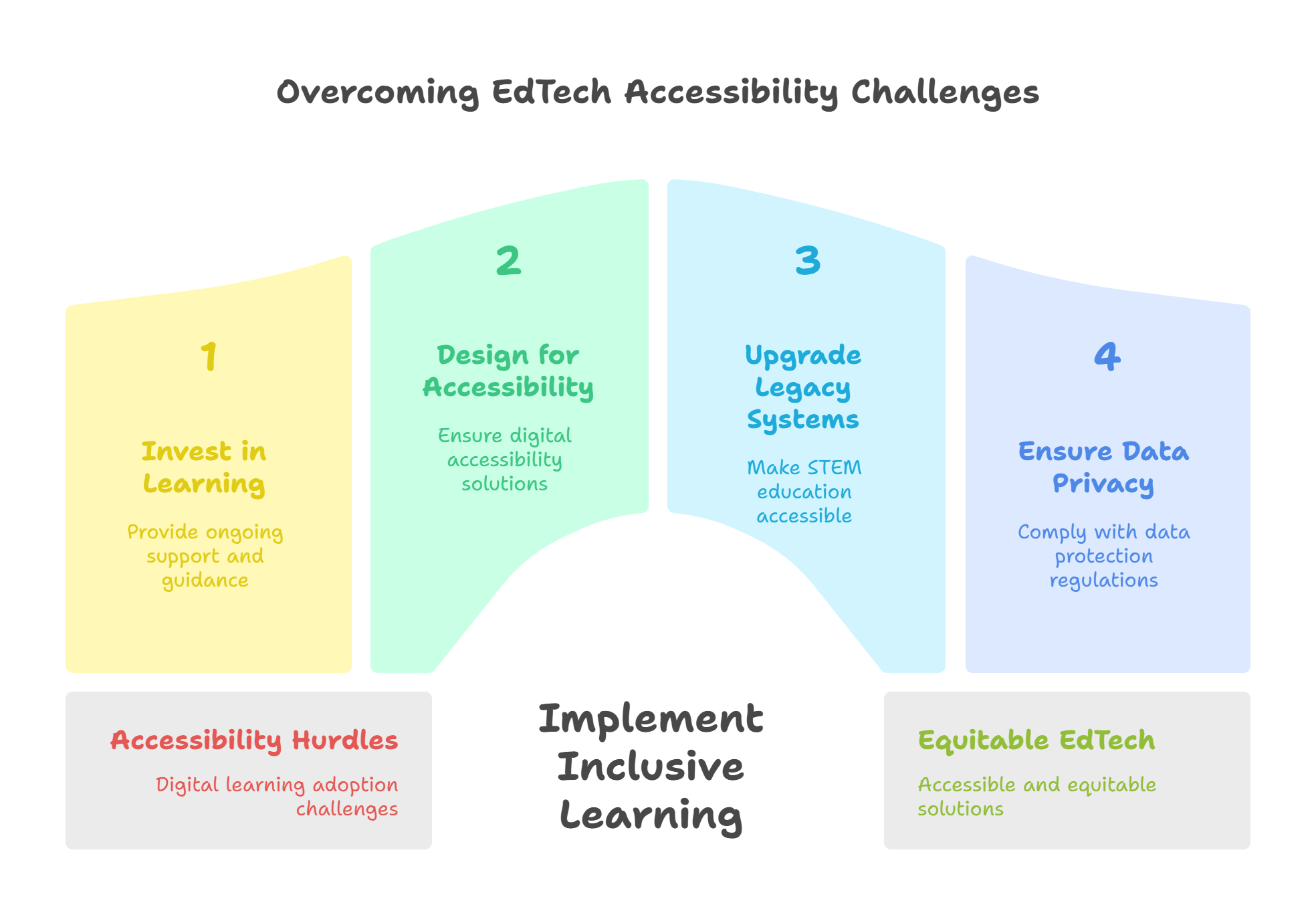
Challenges of Accessibility for EdTech Solutions
Educational technologies have revolutionized L&D, especially for STEM subjects. While digital accessibility is getting widely adopted, the path is full of hurdles. Before you implement inclusive learning, it’s crucial to address these challenges to make EdTech solutions more accessible and equitable.
Let’s quickly check out the roadblocks:
1. Resistance to Accept Change
Despite the widespread adoption of EdTech, several STEM educators remain hesitant to accept his transformation.
This resistance has several reasons, but lack of skills and proper training remains at the top. Many educators and students feel overwhelmed by the complexity of advanced tools. The lack of confidence and familiarity results in resistance and anxiety.
The Solution: Invest in professional learning and development. Ensure you provide ongoing support and guidance to educators to make the integration of EdTech tools seamless.
2. Deep Digital Divide
The digital divide is a major obstacle to implementing EdTech solutions for accessibility. From unstable internet connections to incompatible devices, the digital divide restricts opportunities and outcomes for learners with disabilities.
The Solution: Ensure EdTech solutions are designed for digital accessibility.
3. Integrating Legacy Technologies
EdTech tools are evolving rapidly. However, most existing devices are not sophisticated enough to seamlessly integrate educational technologies. This results in disrupted workflow, data inconsistencies, and technical glitches, creating a poor learning experience.
The Solution: Upgrading the legacy systems to make STEM education more accessible and equitable.
4. Data Security and Privacy
Data theft and security are major concerns, especially when it comes to digital accessibility for STEM education. Protecting sensitive information about students’ disabilities is paramount to ensure data privacy.
The Solutions: Collaborate with EdTech tool developers to comply with data protection regulations such as COPPA or FERPA. Moreover, data encryption should be included, and regular audits should be undertaken for improved results.
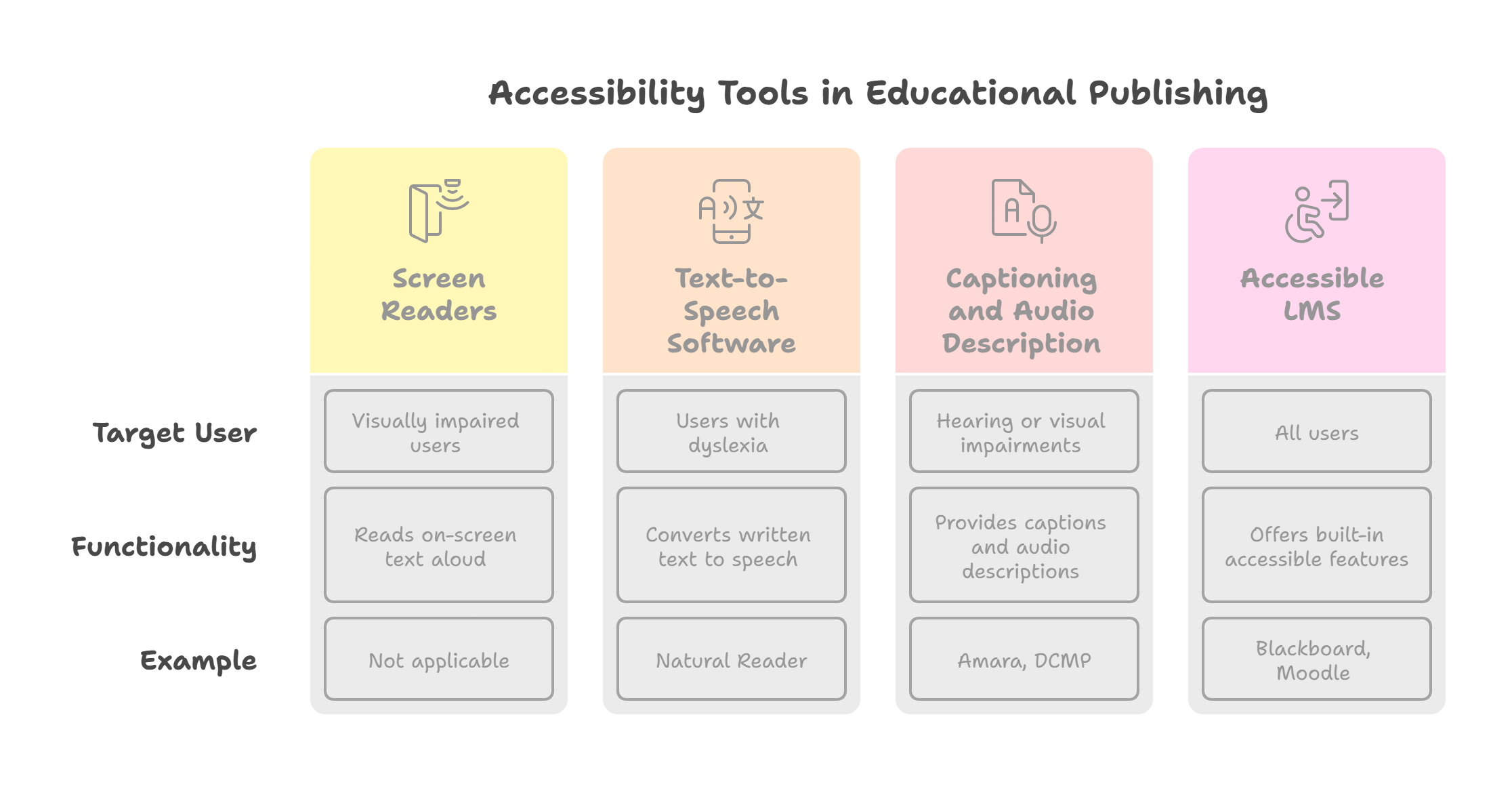
Accessibility Tools and Technologies in Educational Publishing
In educational publishing, a range of tools and technologies play critical roles in enhancing content accessibility. Accessibility consultants often recommend several key solutions to ensure materials are universally accessible:
1. Screen Readers
These tools are used to read out text appearing on the screen for visually impaired users. They make the content of digital programs both perceivable and understandable.
2. Text-to-speech Software
This includes software programs like Natural Reader, which transform written text into spoken word and are designed for people with dyslexia or other reading challenges.
3. Captioning and Audio Description
Captioning and audio description services provided by companies like Amara and the Described and Captioned Media Program help make audiovisual content usable with assistance for people with hearing or visual impairments.
4. Accessible LMS
Learning Management Systems like Blackboard and Moodle have built-in accessible features, and anyone can use assistive technologies.
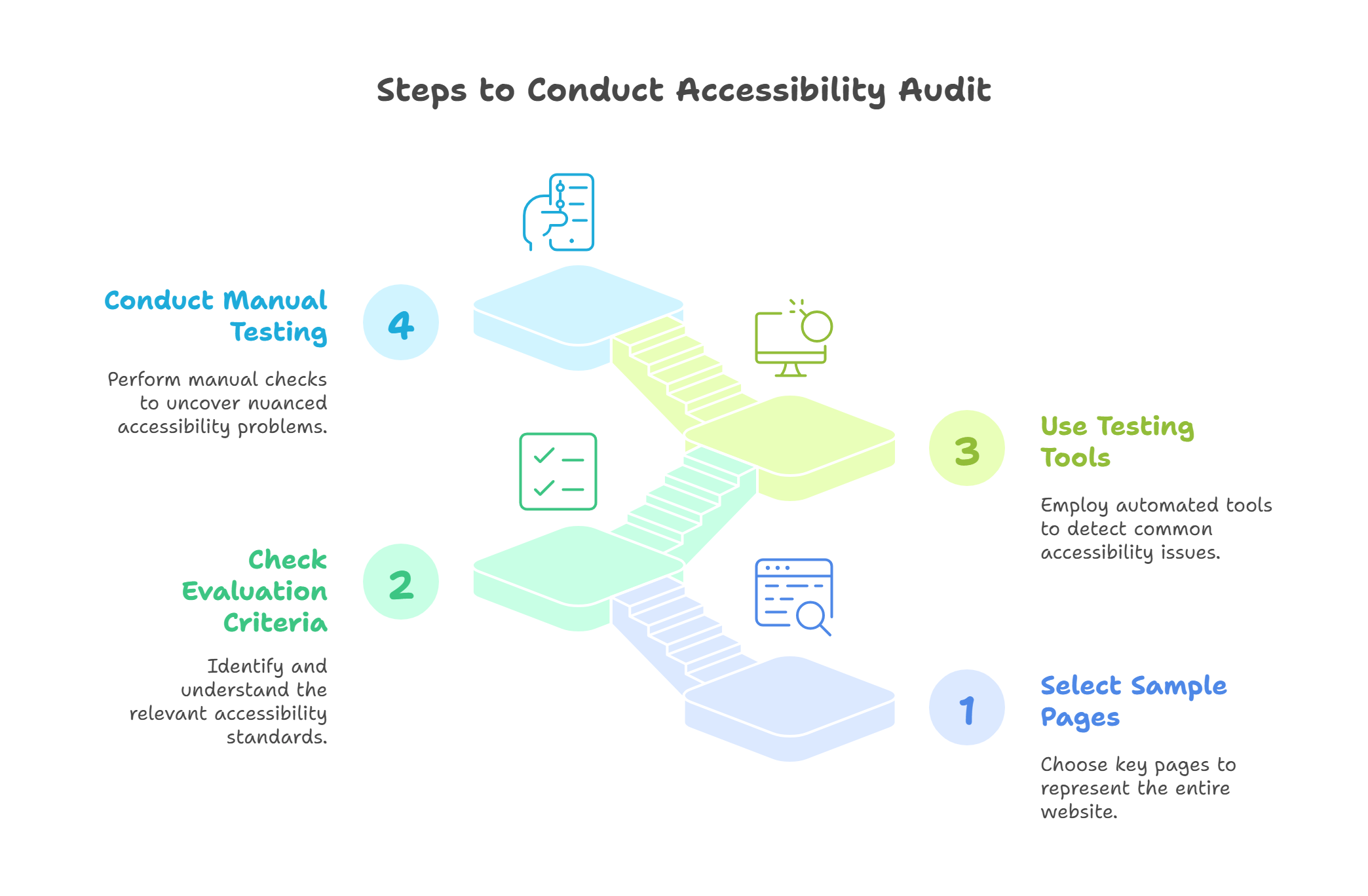
How to Conduct an Accessibility Audit?
Here are steps to follow for conducting an effective accessibility audit for your EdTech solutions:
1. Select Sample Pages
While conducting the accessibility audit, it is not necessary to audit every website page. You can select some sample pages and check them to ensure they are accessible.
The sample pages can include some of a website’s important pages, such as the homepage, contact pages, legal information, etc.
However, regarding educational platforms, all the information, learning, and text content must also be checked for accessibility. While checking the text content, focus on headings, font size, font color, and background color.
2. Check Evaluation Criteria
Indicate which accessibility guidelines and standards your EdTech solution has to follow. This often includes international standards such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
These recommendations offer specific standards for ensuring that web material is accessible to individuals with disabilities.
3. Use Testing Tools
Use automated accessibility testing tools to find frequent problems, such as poor color contrast, missing alternate text for images, and navigational difficulties.
By doing this, you’ll speed up the testing process and have more time to focus on some of the more complex and specialized aspects of accessibility audits.
4. Conduct Manual Testing
Use automated accessibility testing tools to identify common issues such as low color contrast, missing alternate text for images, and navigational challenges. This will expedite the testing process and allow you to concentrate on some of the intricate and specialized components of accessibility audits.
Moreover, it is essential to combine manual testing with automated technologies. Manual testing entails using tools like screen readers to interact with specific sample websites to verify compatibility.
This procedure is essential for identifying small difficulties with accessibility, like keyboard accessibility, logical reading sequence, and appropriate ARIA roles, that automated tools could overlook.
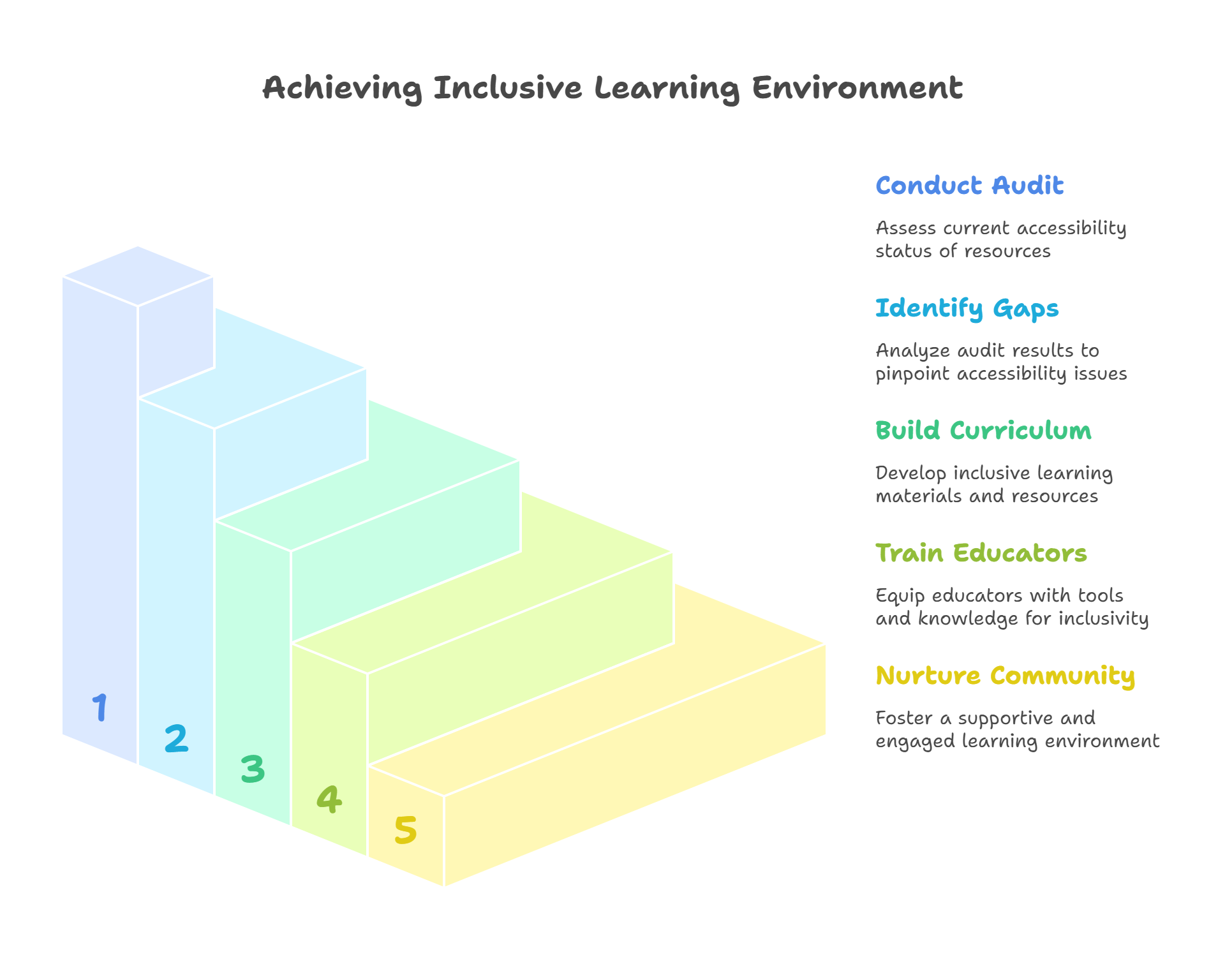
Steps to Implement Accessibility Solutions Effectively
Educational institutions must follow this structured process when shifting to an inclusive learning environment.
Here’s a playbook to turn an inclusive vision into reality:
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Accessibility Audit
The first step for universities is to understand where they stand on the accessibility spectrum. They need to conduct a comprehensive, professional audit of all web-related resources, accessible to learners.
Here are the four pillars for a successful accessibility audit:
- Organizations can invite per spectrum of students with disabilities to review all the existing digital resources. This valuable feedback can be converted into data-driven insights into the gaps and needs of learners.
- Today, the market offers many tools and technologies that enable comprehensive and effective testing of all digital products. The institute’s websites, apps, and the institutes’s digital library of resources, must undergo comprehensive accessibility checks.
- Institutions may not have the experts used to conduct audits professionally. There is merit in partnering with experts in accessibility solutions.
- Accessibility audits cannot be a one-time process. They need to be conducted regularly, especially as institutions as new resources.
2. Identify Accessibility Gaps
The results of the accessibility audit must be translated into a comprehensive report of where the gaps in accessibility lie. Institutions must be able to pinpoint exactly how these gaps affect students with diverse disabilities. The range of disabilities comprises visual, hearing, cognitive, intellectual, motor, and learning challenges.
3. Build an Inclusive Curriculum & Accessible Learning Resources
Traditional curricula do not account for the needs of learners with disability. The lecture-style learning system, along with physical textbooks, leaves out this entire demographic of students.
Organizations must work towards bridging the gaps through the introduction of digital resources that are powered by accessible solutions. For instance, students with disabilities must have access to a fully accessible digital library of on-demand resources. For example, they must come with features such as video captions, read-aloud audio, and alternate text for non-text content such as images.
4. Train and Equip Educators with the Right Tools
Educators, who form the backbone of educational institutions, must have access to structured training around the need for and usage of inclusive learning environments.
For example, they must be sensitized to the needs of students with disabilities and the gaps and their impact on students in the existing system. They must also have training on how to use accessible learning systems to generate inclusive content that can power engagement for all students.
5. Nurture a Strong Community
It’s not enough to provide students with disabilities with learning resources. Institutions need to nurture a strong sense of community so learners can stay engaged and feel supported.
They can receive mentorship, connect with their peers and alumni, and build a voice on campus. Building strong networks that enable mentorship opportunities, internships, and exposure to the industry plays an important role in providing holistic education to learners with disabilities.
Final Words
Educational institutions that make early investments in accessible solutions can appeal to a wider range of students.
By partnering with an expert in technological innovation, they can undertake a structured shift towards inclusive education. In turn, they can reap the benefits of higher enrollments and student retention rates, comply with disability laws, and build a reputation as a provider of equal opportunity.
If your institution aims to transition into a center for inclusive learning, consider investing in the right technology to power this shift. Hurix Digital comes with expertise in building large-scale accessible learning systems.
With our advanced solutions, we can help your institution create a learning environment that embraces diversity and fosters academic success for all students. Together, let’s build the future of education—one that is inclusive, accessible, and equitable.
Get in touch with us to start a conversation.
Summarize with:

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful