A Guide for Modern Educators to Design Inclusive and Future-Ready Curriculum
Summarize with:
Higher education is expected to have a global value of $860.11 billion by 2030. What does that mean for students and teachers worldwide? Academic concepts, such as curriculum and eLearning design, will be at the forefront of the education industry. Curriculum design in education can be defined as a thinking process that explains how teachers want students to learn.
The better the curriculum is designed, the easier it will be for students to learn. As this process is of the utmost importance, every educational institute must understand it to create an efficient educational program.
However, contemporary curriculum design needs to consider additional factors. For instance, the number of mobile phone users globally is estimated to grow to 7.49 billion by 2025. Hence, the growth of mobile penetration demands that educational material take a mobile-first approach to learning.
In this blog, we deconstruct curriculum design, the different types, and how to make the process relevant to the needs of today’s learners.
Table of Contents:
- Different Types of Curriculum Design
- What is Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) in Education?
- Why is DEI in Education important?
- Seven Steps in Curriculum Design
- 4 Pillars of Contemporary Curriculum Design
- How to Use AI to Make Effective Curriculum Design?
- 8 Ways to Infuse Diversity and Inclusivity into Your Curriculum Design
- Start with Self-Reflection
- Incorporate Diverse Perspectives Into Course Materials
- Foster an Inclusive Classroom Culture
- Address Bias Timely
- Use Inclusive Language and Imagery
- Leverage Technology for Accessibility
- Provide Cultural Competency Training for Instructors
- Use Feedback to Improve Inclusivity
- In Conclusion
Different Types of Curriculum Design
The process of curriculum design and development takes a lot of effort as the creator needs to consider many aspects. There are three types of curriculum designs, and each serves a different purpose.
Read on to learn the unique benefits of each kind.
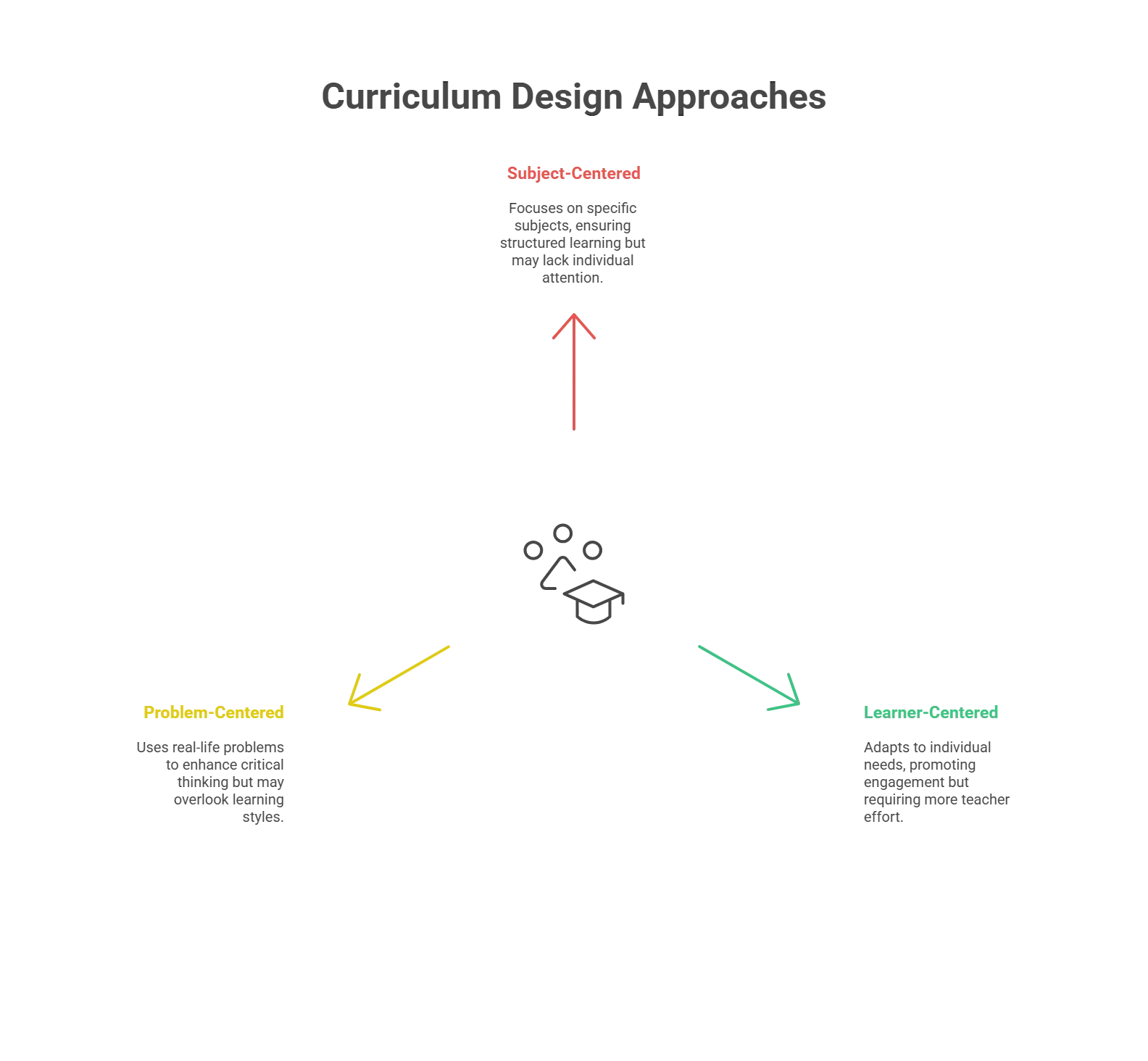
1. Subject-Centered Curriculum Design
As the name suggests, this type of curriculum strongly emphasizes a particular subject. It can be literature, mathematics, or any other subject. This type of design highly inspires K12 curriculum because it specifies what should be studied and how to make things easy for students to follow.
However, the student’s unique learning preferences are not considered while creating this curriculum design. As a result, there may be issues with motivation and involvement on the part of the learners, and they might even lag behind academically.
2. Learner-Centered Curriculum Design
Learner-centered curriculum design considers each individual’s needs, interests, and ambitions. It simply recognizes that every learner is unique and adapts to their needs.
A learner-centered curriculum design aims to give students control over their education and equip them with the freedom to make informed decisions.
However, this curriculum creation method can be labor-intensive. It is the teacher’s responsibility to develop differentiated education to meet each student’s need for learning and identify materials that support that instruction.
Teachers must balance the needs and interests of the students in order to develop a curriculum that is learner-centered, which is quite a challenging task to accomplish.
3. Problem-Centered Curriculum Design
In this type of curriculum design and development, real-life problems are used to sharpen the learners’ minds. This curriculum enables students to analyze a situation and find a solution.
This also fosters the growth of creative thinking in learners, which later helps them in their careers.
However, this method of curriculum design has the issue of not always considering learning styles. The educator needs to be mindful throughout to make sure that all the students are learning the course effectively.
What is Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) in Education?
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion, or DEI in education, refers to the policies and practices that help create learning environments that embrace the differences among students from diverse backgrounds.
Diversity encompasses students of various races, ethnicities, genders, abilities, backgrounds, cultures, and sexual orientations.
Equity refers to the fair distribution of resources and opportunities to help students reach their full potential. By prioritizing equity, educators can help close the achievement gap and promote equal access to educational resources for all students, regardless of their diverse backgrounds.
Inclusion refers to the extent to which students feel a sense of belonging in the classroom. Inclusive teaching practices recognize that every student has unique needs and learning styles and seek to meet these needs in the school.
Why is DEI in Education important?
The impact of DEI in K12 and higher education is tremendous, whether in improving learning outcomes or shaping students’ development as empathetic human beings.
Over the years, various schools and universities have conducted studies on the values of DEI in schools and found the following results:
- Learning with people from diverse backgrounds and cultures in the classroom leads to a better understanding of the subject matter.
- Diverse classrooms foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills, especially when applied to real-world problems.
- Exposure to diverse cultures helps develop tolerance and a greater sense of security in environments where foreign cultures are present.
- Diverse classrooms promote intercultural sensitivity and allow students to learn about other languages and cultures.
- Creating awareness and personal connections with diverse cultures in the school can prevent the development of prejudices later in life and foster empathy with others.
- Diversity and inclusion in higher education better prepare students for the global workforce, where they must work with people from different cultures and social groups.
Seven Steps in Curriculum Design
Now that you understand the fundamentals of curriculum design, let’s see how it should be created:
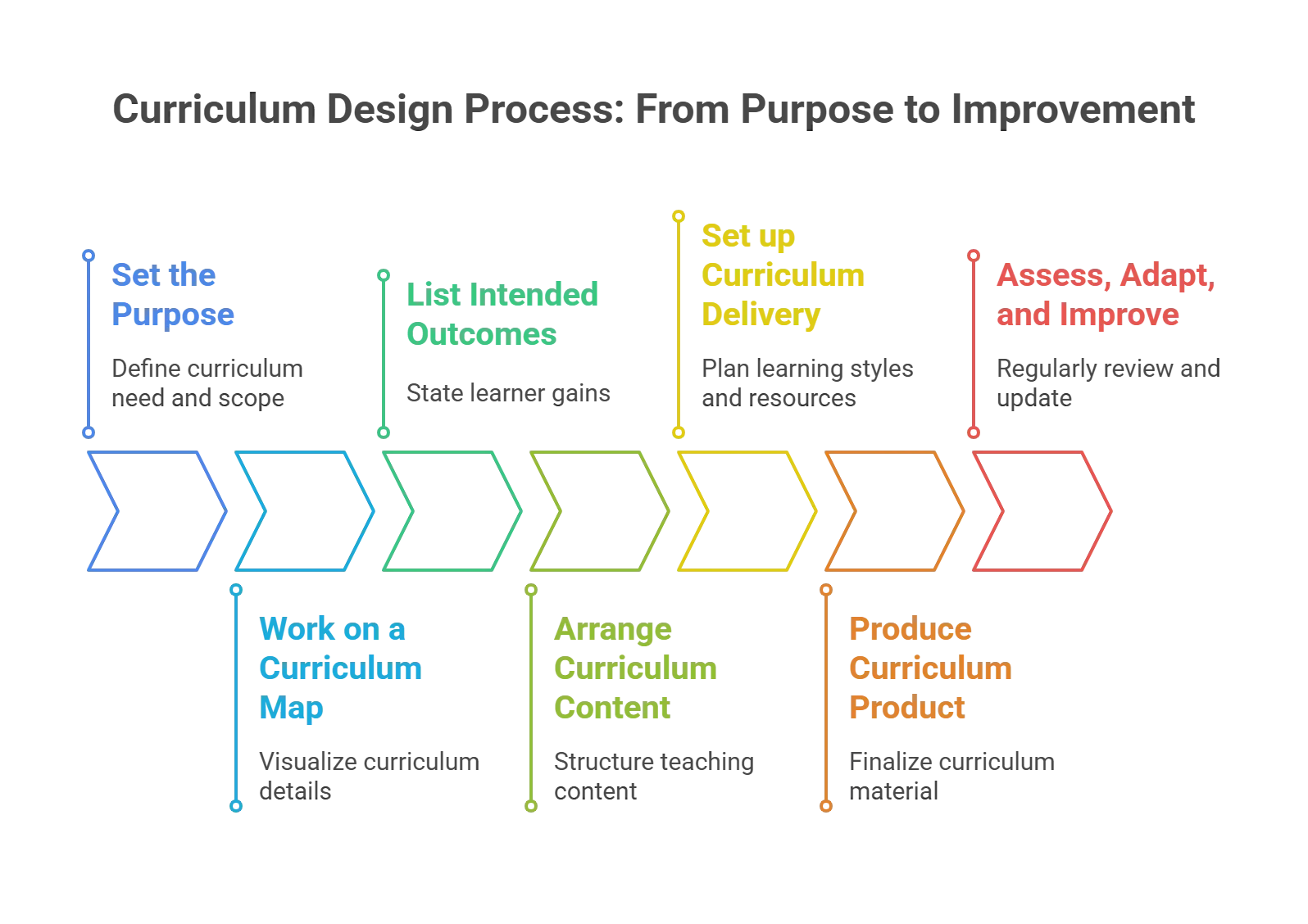
Step 1: Set the Purpose
What is the need for your curriculum? What problems and issues are you targeting? What do your students need?
Ask such questions before trying to design your curriculum. This will help you scope the program effectively. Moreover, it will help you integrate the school’s guidelines, context, and educational policies by the government.
Step 2: Work on a Curriculum Map
It is always ideal to get a visual representation of your ideas. The same goes for curriculum design in education.
Add necessary details, such as deadlines, student progress, exams, and activities. Mapping the curriculum gives you an overview of what to do, exposing areas that need more work. You can even involve curriculum providers to get an expert assessment of the situation.
Tip: Create a student entitlement for better results. Also called pupil offer, a student entitlement should focus on broadening the curriculum. It can include enrichment experiences, such as extracurricular activities and educational visits.
Step 3: List the Intended Outcomes
Now, it is time to state the intended outcomes that a learner will gain by participating in curriculum design.
This section should include the defined outcomes, the components surrounding the outcomes, some examples, and an overview of learning tendencies.
Step 4: Arrange Curriculum Content
This is the meaty part of the process, as you will decide the whats, whens, and whys of teaching.
You will also select the subjects and concepts the curriculum will cover. You should also consider how these aspects interconnect with other subjects, which will require a further breakdown of the components.
Thus, the content must be carefully structured, revamped, and designed.
Step 5: Set up the Curriculum Design Delivery
Now that the educational program design is taking form, you need to plan its delivery. This step will focus on picking learning styles, activity design worksheets, and different delivery modes.
Another crucial part of the step is picking the right resources. Focus on using high-quality ad hoc resources and equipment to keep the curriculum top-notch.
Step 6: Produce Curriculum Product
Once everything is finalized, the production of the curriculum material will take place. You should find suggestions from existing materials for better evaluation. During this step, you will also set up the assessment criteria to track the course’s growth.
Step 7: Assess, Adapt, and Improve
A process as complex as curriculum design might take some review and revamping.
In the final step, you ensure the sustenance of the educational program by regularly reviewing it. You make adaptations wherever needed, keep up with the latest policies and programs, find better methods, etc.
Keep the curriculum up-to-date with industry standards to ensure you are producing well-equipped learners.
4 Pillars of Contemporary Curriculum Design
Today’s learners comprise a wide range of audiences, and curriculum designers must keep diverse needs in mind. Here are four rules for inclusive, holistic curriculum design that can boost learning effectiveness:
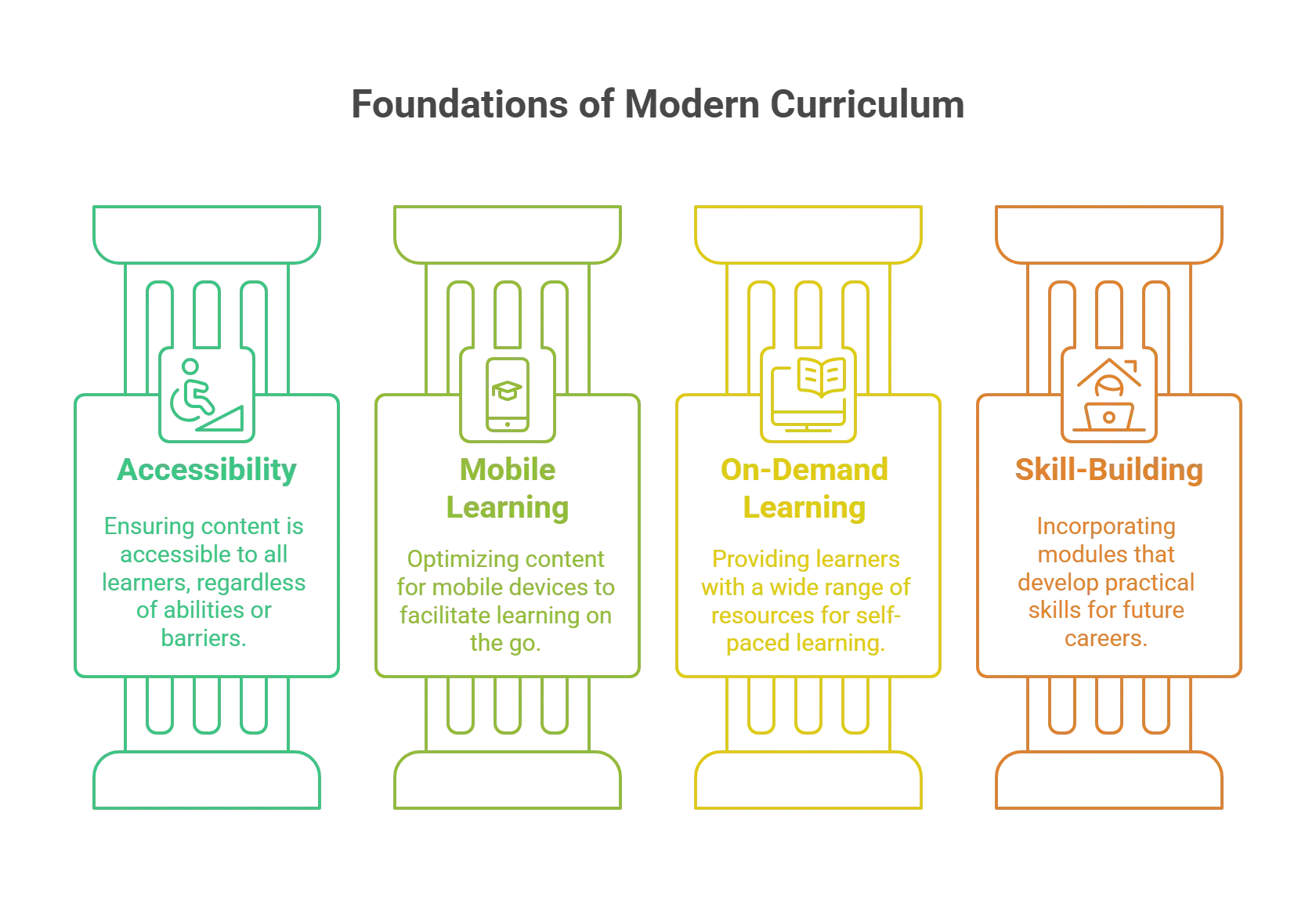
1. Optimize for Accessibility
Curriculum designers must ensure that the content is optimized for accessibility for learners with diverse needs, including those with disabilities, learning limitations, and language barriers.
2. Optimize for Mobile Learning
The content must be optimized for mobile usage. For instance, the introduction of byte-sized multimedia resources enables micro-learning from one’s cell phone, even in low/ no connectivity areas.
3. Access to On-Demand Learning
Learners must have access to a wealth of on-demand learning resources, which nudges them towards self-learning, quicker absorption of concepts, and more opportunities to practice.
4. Design for Skill-building Opportunity
Skill-building is of growing importance to learners, from programming and design to social media management. Curriculum design must include modules that enable skill-building. For example, the introduction of life-simulated environments helps nurture skills cost-effectively and comprehensively.
How to Use AI to Make Effective Curriculum Design?
Let’s see how you can use the power of AI to make your curriculum design indispensable:
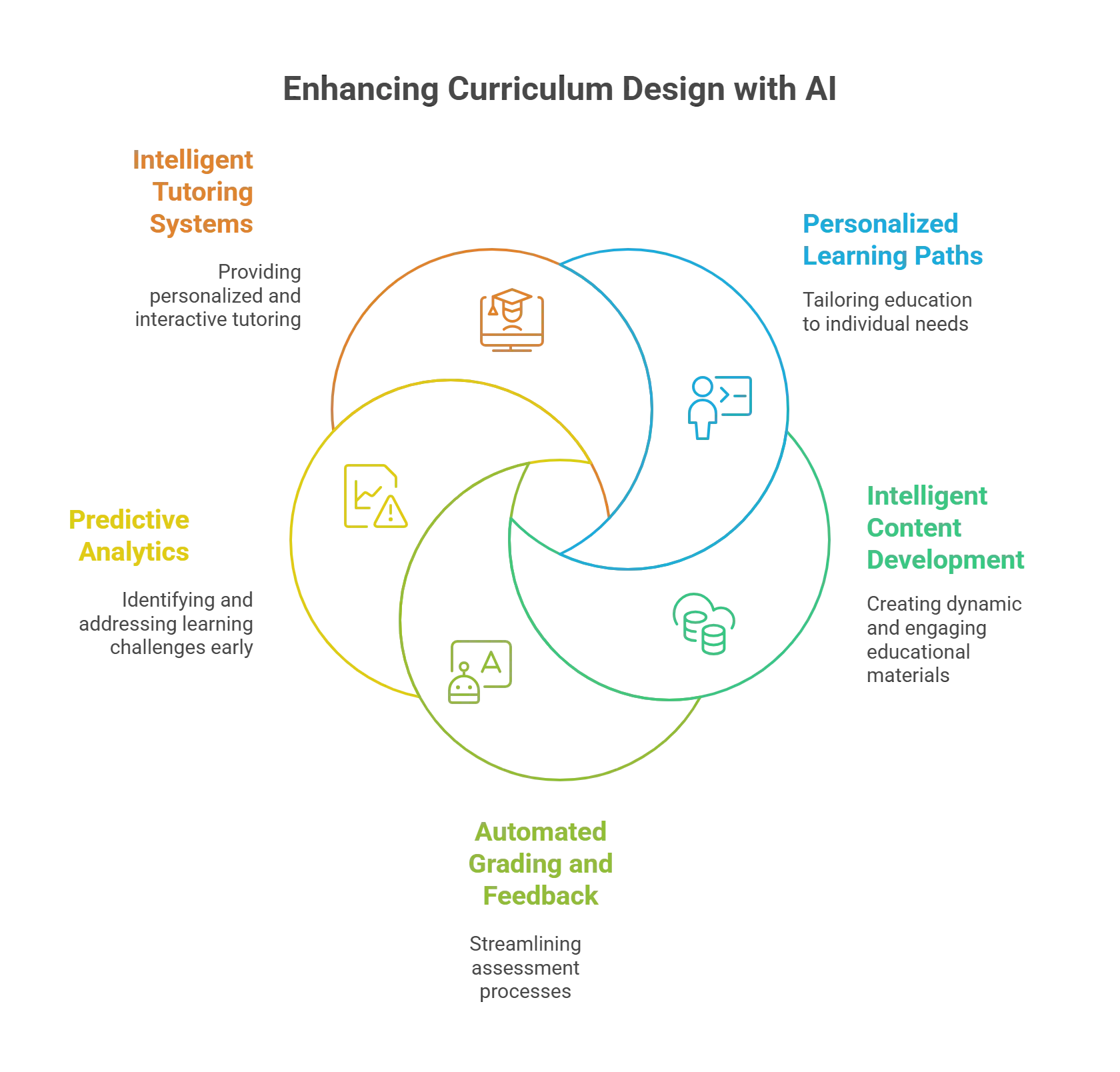
1. Personalized Learning Paths
Traditional learning is designed to offer a one-size-fits-all approach. On the contrary, AI-powered systems utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, including students’ learning preferences, weaknesses, and progress. This analysis helps tailor instruction to the learner’s requirements.
AI algorithms recommend appropriate resources, activities, and assessments through a data-driven strategy that continuously monitors a student’s performance. It uses predictive analysis to adapt the content according to an individual’s level of expertise.
Machine learning in education can detect if a student encounters difficulties with a new concept and offers additional resources while adapting the material to suit the difficulty level, facilitating their understanding of the concept. Conversely, if a student is advancing rapidly, AI can dynamically adjust the course pace to align with their learning speed and present more challenging tasks to keep them engaged.
AI in curriculum design creates robust learning solutions and customized journeys that mirror individual learner interests, preferences, and needs. AI learning modules reinforce concepts by filling in knowledge gaps while catering to distinct abilities to optimize their learning journey.
Educators may monitor and assess students’ progress in real-time and modify their pedagogical approaches to support individualized instruction tailored to each student.
2. Intelligent Content Development
Where students learn best through visual aids, relying solely on traditional text-based content may fail to achieve desired outcomes and engage learners. AI’s intelligent content creation goes beyond traditional teaching methods by providing dynamic 2D-3D visual aids and simulating real-life experiences through web-based study environments, allowing students to perceive information in multiple ways.
With the vast amount of data at their disposal, educators may find it overwhelming to identify the most relevant and engaging resources for their students. With AI, course developers may leverage an extensive library integrated with stock assets and pre-made templates optimized for preferred learning modalities. Infusing AI capabilities such as automatic translation in curriculum development facilitates multilingual content creation with reduced time and greater accuracy.
As advancements in AI emerge, AI algorithms examine content from multiple sources, including textbooks, online material, and educational databases, to curate a diverse and comprehensive assortment of resources aligned with the curriculum.
AI-powered content curation enables educators to provide students with high-quality coursework that supports their learning objectives. It also ensures that the content remains relevant to students’ evolving needs and the changing educational landscape.
3. Automated Grading and Immediate Feedback
The grading of homework and assignments can be time-consuming and detract from valuable teaching and learning time otherwise dedicated to class preparation. Machine Learning merged with AI streamlines these processes, eradicating the need for manual grading and logging into multiple programs to review student work, track progress, and provide feedback.
AI technologies offer a more efficient and objective approach to assessment and feedback, enabling educators to allocate their time more effectively. Educators can focus on their core responsibilities, ultimately enhancing the teaching and learning experience.
AI-powered solutions add value to the education system by centralizing and automating administrative tasks, such as grading assignments, monitoring attendance, and maintaining student records. AI-integrated grading systems accurately evaluate exams and generate prompt results.
The transparency of the AI grading system reduces bias in grading and ensures consistent and fair evaluations and efficient outcomes, sparing no room for external manipulation. Educators may leverage the valuable insights offered by an AI curriculum for schools to adapt the course accordingly for enhanced comprehension and retention.
4. Predictive Analytics Promote Early Intervention
Distinguishing effective teaching from merely providing content lies in including continuous feedback. Analyzing reports based on everyday data is an integral aspect of this feedback process undertaken by AI.
Machine learning algorithms identify patterns and trends in student performance while generating predictive models that identify early warning indicators. AI-powered predictive analytics helps educators identify and address areas of strength and weakness at individual and class levels by examining various data points, such as attendance records, assessment results, and learning behaviors.
Real-time formative assessment tools can reduce dropout rates by detecting students at risk of falling behind or experiencing difficulties in specific subjects. The data-driven feedback and predictive model enables educators to intervene when required and undertake informed decisions about instructional strategies for providing targeted support where needed.
5. Intelligent Tutoring System
In a conventional setup, student assistance relies on a group of standard questions and answers. However, the AI curriculum for K12 utilizes intelligent digital technologies to provide an individualized and interactive learning experience by simulating one-on-one tutoring sessions.
Virtual tutoring and assistance use natural language processing, machine learning, and cognitive modeling to imitate human conversation and provide personalized guidance, feedback, and support. By integrating AI capabilities, Learning Management Systems gain enhanced abilities to understand and address unconventional requests, analyze and respond to conversational text with relevant data, and extend open-format responses.
Chatbots are a well-known illustration of how AI in education leverages data to enhance knowledge and offer appropriate assistance. Conversational AI systems excel in delivering intelligent tutoring by closely observing patterns in content consumption and tailoring their approach to meet individual needs. AI-based digital tutors allow students to receive real-time explanations and guidance without engaging with human tutors.
An AI-based intelligent tutoring system leverages the student’s previous responses to determine the most relevant questions to ask. It includes targeting areas where the student has struggled by incorporating pertinent questions or progressing to a higher level when correct answers are consistently received.
Utilizing AI in curriculum design through ITS can offer additional practice exercises, explain concepts in various ways, and track progress in real-time for students who have trouble understanding algebraic equations, for instance. A personalized approach to tutoring consolidates understanding and helps students overcome challenges at their own pace.
8 Ways to Infuse Diversity and Inclusivity into Your Curriculum Design
Here are some ways to promote DEI in your curriculum design:
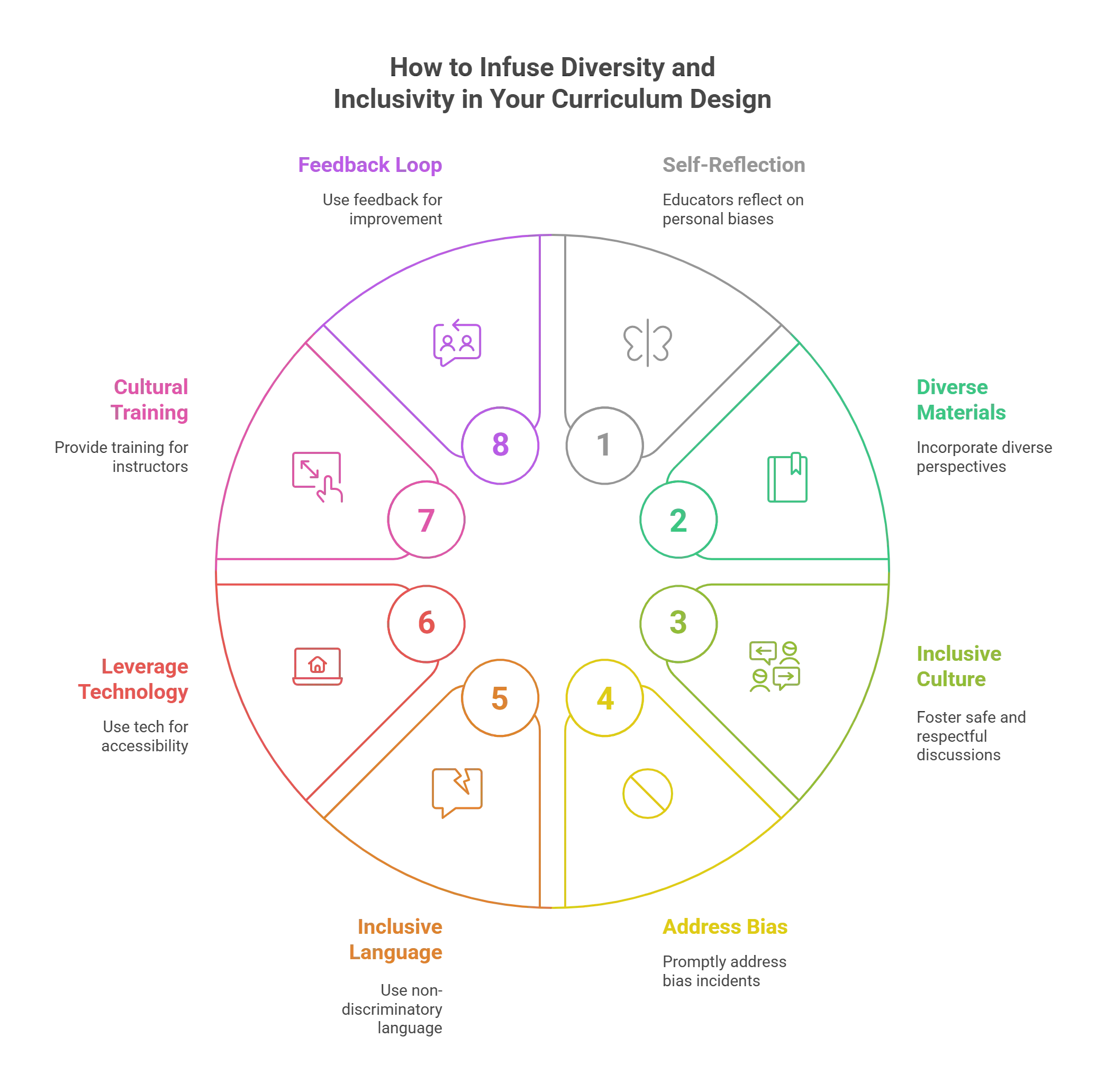
1. Start with Self-Reflection
Before teaching diversity and inclusion to students, take a step back and reflect on your own biases and assumptions. Everyone has biases, and acknowledging and understanding them is the first step in creating an inclusive learning environment.
2. Incorporate Diverse Perspectives Into Course Materials
One of the best ways to promote diversity and inclusivity in schools is to incorporate diverse perspectives into course materials. This can be done by adding opinions and philosophies of various authors, artists, and experts from diverse backgrounds to the reading material.
However, it must be ensured that these materials are not just a token representation of diversity. They should be authentically integrated throughout the course, not as an isolated incident.
3. Foster an Inclusive Classroom Culture
Besides integrating DEI into the course, it’s also important to provide a safe space for students to discuss issues related to diversity and inclusion. Encourage students to share their experiences and perspectives in the classroom and ensure that they feel safe and respected when discussing sensitive topics.
Additionally, create opportunities for students to interact and learn from each other through physical or virtual collaborations. It helps promote a sense of community and belonging.
4. Address Bias Timely
To ensure that all students are respected, educators must set clear expectations for behavior and address any instances of bias or discrimination promptly and appropriately.
Addressing bias does not mean shaming the other. Instead, it means generating awareness about biases in our minds. Once people recognize their biases, they can take steps to eliminate such harmful thinking.
5. Use Inclusive Language and Imagery
Another important aspect of inclusive curriculum development is using non-discriminatory language. Educators must make sure to avoid gendered language and use gender-neutral pronouns instead.
Similarly, stereotypes and derogatory terms must be removed from the K12 curriculum. It’s also vital that images and other visuals used in course materials reflect diversity in the community and do not perpetuate harmful stereotypes.
6. Leverage Technology for Accessibility
eLearning in higher education has become a common phenomenon in today’s digital era. Modern digital curriculum providers offer newer technologies and accessible solutions that make course content accessible for all groups.
They provide features such as closed captioning and transcripts for videos and audio recordings, multiple formats, and compatibility with screen readers, enabling students with visual or auditory impairments to access them.
They also provide multiple–language translations for course materials to help non-native speakers better understand and engage with the content. Educators can leverage them to promote DEI in higher education.
7. Provide Cultural Competency Training for Instructors
Providing cultural competency training for instructors is another crucial step for ensuring diversity and inclusion in schools. The areas of training should include:
- How to create inclusive course material?
- How to facilitate respectful discussions about sensitive topics?
- How to address bias or discrimination in a live or virtual setting?
Such training can help ensure educators are equipped to create an inclusive learning environment and appropriately address instances of bias or discrimination.
8. Use Feedback to Improve Inclusivity
Finally, remember to take feedback from students on course materials and group discussions. You can use the feedback to make improvements and adjustments and create a truly diverse and inclusive learning environment.
In Conclusion
According to the World Economic Forum, education is an industry that will produce over 800 million K12 graduates by 2030. To keep up with this growth spurt, educational institutions will require an additional 1.5 million teachers annually.
However, the need for elevation won’t stop at human resources, with developing economies like Africa and Asia leading the expansion. It will require a redesign of technologies and concepts, such as curriculum design.
Since the process involves students’ academic learning, it requires vast knowledge and skills for impeccable execution. That is why names like Hurix help institutions easily curate their curriculum design.
With 20 years of experience assisting education technology companies, Hurix Digital is one of the best global curriculum providers. Contact the experts today to curate your curriculum efficiently.
Summarize with:

Senior Vice President – Business Development
at Hurix Digital, with over 25 years of experience in EdTech and workforce learning. He excels in business development, customer relationship management, and scaling digital learning solutions, driving global growth through innovative content, simulations, and AI‑driven training offerings
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful