The Role of Accessibility Consultants in Creating Inclusive Education
Summarize with:
A web accessibility audit report is of utmost priority and concern within the higher education system, considering the increased usage of digital technologies in learning and teaching. Students are expected to have complete access to online learning environments, course materials, and communication tools regardless of physical and cognitive abilities.
It would be difficult to believe but 96% of higher education websites are failing to meet basic accessibility standards. In February 2022, a report by AAAtraq revealed that nearly every website across 2,000 U.S. colleges and universities falls short of the Web Content
Accessibility Guidelines 2.1 standards.
What’s even more appalling? Specifically, 13% of these institutions will be at an extremely high risk of legal action, while almost half will experience high legal risk. A mere 4% have done what is required to be placed in the ‘low risk’ category. Thus, if you are an educational institution leader, this should be your wake-up call.
To take any action in the right direction, first, you must determine where your institution stands in terms of web accessibility. Web accessibility audits can give you a clear picture of the barriers that might lock out students with disabilities from accessing your online resources.
When it comes to accessibility audits, there are two options. One can choose either manual auditing or web auditing using automated tools. Both have advantages and limitations, which we’ll explore in greater detail throughout this article.
Table of Contents:
- What is Web Accessibility?
- The Importance of Web Accessibility for Education
- How to Ensure Web Accessibility within Higher Education
- Manual Web Accessibility Audits: Advantages and Limitations
- Automated Tools for Web Accessibility Audits: Advantages and Limitations
- How to Prioritize Web Accessibility Improvements on a University Budget?
- Raise Awareness
- Show Return on Investment
- Strategize an Accessibility Policy
- Get Funding for Accessibility
- Conduct Automated and Manual Testing
- Gather and Act on User Feedback
- Make the Most of your Accessibility Budget
- Leverage Technology for Affordable Accessibility
- Conduct a Comprehensive WCAG Audit
- Conclusion
What is Web Accessibility?
Web accessibility means designing websites so that students can access content without obstacles, regardless of ability. As reported by the 2000 U.S. Census, about 20 percent of Americans have disabilities that limit their use of the Internet.
With increased dependency on the Internet, web accessibility is an urgent necessity. Higher educational institutions must ensure their digital learning resources are accessible to all students, faculty, and staff.
This will help them in:
- The fulfillment of their social responsibilities.
- Establishment of accessibility standards
- Increase student satisfaction and interest in the institutions.
- Enhancing diversity in the student population and accelerating the overall levels of enrollment.
The Importance of Web Accessibility for Education
Accessibility in the context of web applications is a must-have when it comes to education rather than being a luxury. It makes certain that none of the children falls behind the rest because of incompetence, disability, or learning difficulties. But why is it so desirable?
Firstly, it’s about inclusivity. When the content is available, students with disabilities related to visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments have opportunities. This empowers them to learn along with fellow students who are in their class without even having to interact with them.
Secondly, it’s about compliance. It is pertinent that in the U.S., educational institutions follow ADA regulations. Various legal consequences may arise from the inability to deliver accessible information and operations to clients, and none of the businesses would want to suffer a negative impact on their reputation.
Lastly, accessible content often benefits all users. Features like clear navigation, well-structured content, and alternative text for images improve the overall user experience.
How to Ensure Web Accessibility within Higher Education
Higher education institutions must follow a strategic approach when preparing for the WCAG accessibility audit. Here are some best practices:
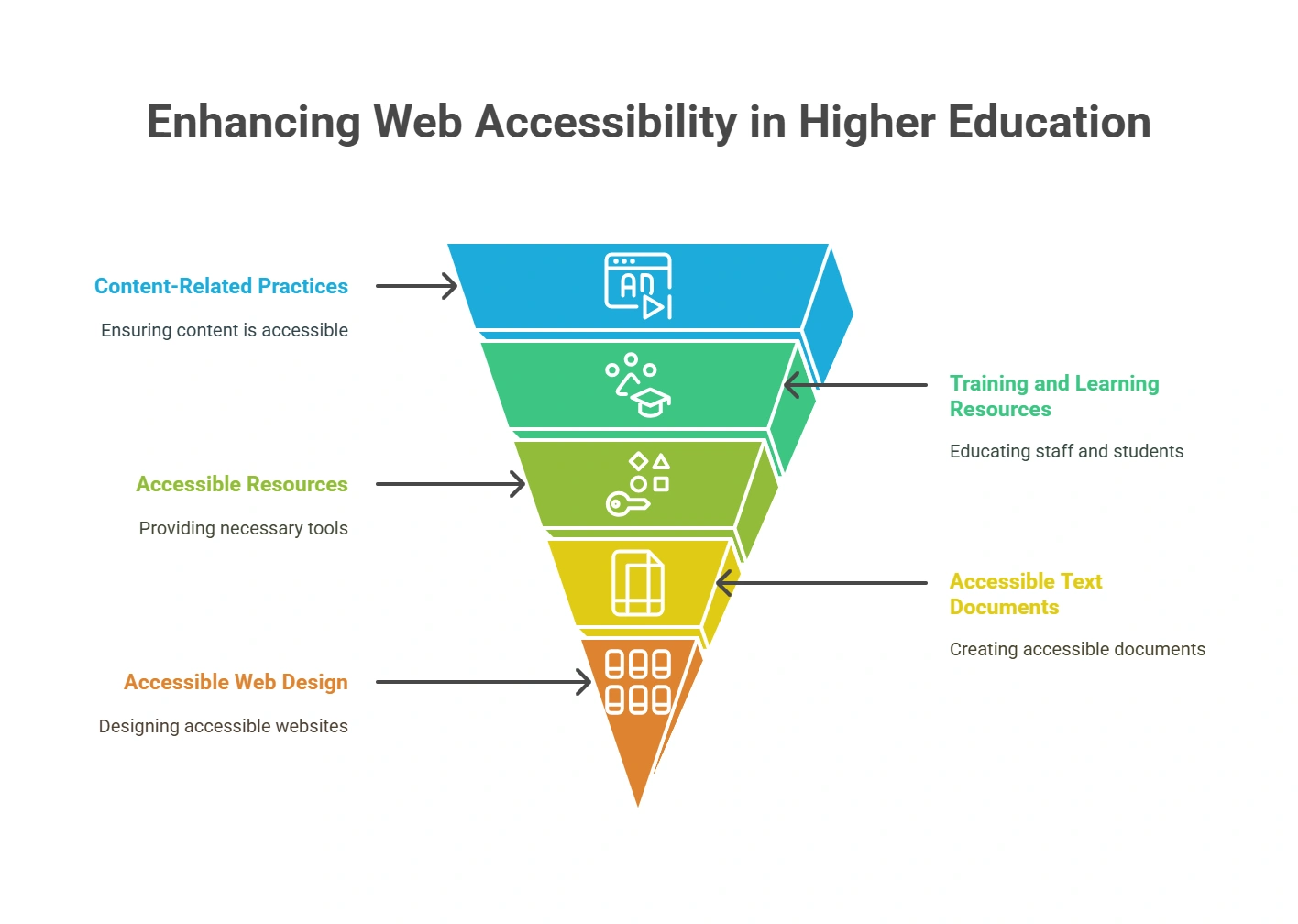
1. Content-Related Practices
First, institutions should emphasize the following practices in inclusive design:
- Alt text for images.
- Captions and transcripts for videos.
- User-friendly navigation of websites.
- Headings in the correct order
- Descriptive hyperlinked text
- Improved color visibility for color-blind users
- Layout tables for easy navigation
- WAI-ARIA (Web Accessibility Initiative — Accessible Rich Internet Applications) for accessible and interactive content.
Such practices mitigate barriers for students with disabilities and increase the accessibility of digital content.
2. Training and Learning Resources
Top management of higher educational institutions must furnish faculty, publishers, and content creators with full training and resources regarding the importance of web accessibility.
Educators need to be prepared to create accessible content. Web accessibility audit reports should be referred to to ensure all students have equal access to learning materials.
3. Accessible Resources
Web accessibility is based on hardware, software, and content, which are integrated to provide an accessible digital space for all.
Higher education institutions can be more inclusive by investing in the best accessibility automation tools, assistive technology-compatible software, and hardware with built-in accessibility within the devices.
4. Accessible Text Documents
Digital documents should be created in a way that is screen-reader-friendly. Digital formats like ePUBs and PDFs should ensure comprehension and readability across devices and formats.
5. Accessible Web Design
Web developers have a crucial role in the facilitation of access to all users of the university website, including those affected by some disability. Their sites should be implemented with the following guidelines on WCAG audit:
- The web-compatible font allows users to modify the text size using their browser and monitor settings.
- High-contrast color schemes to maximize readability.
- All images that provide important information must include descriptive text, called alt text, in the alt attribute.
- Screen readers text aloud feature for visually impaired users.
- Images should not replace text or hyperlinks since some users may use browsers that block images.
- Videos are very prevalent in education; they should include transcripts, captioning, and audio descriptions:
- Captions are to be displayed as text synchronized with video playback at the time of watching.
- Audio descriptions of video content that describe the action happening in a video.
By adhering to these best practices, colleges and universities can ensure that all students have equal access to educational materials and opportunities.
Manual Web Accessibility Audits: Advantages and Limitations
The heads of all educational institutions must know that colleges and universities are the most vulnerable to lawsuits associated with the Americans with Disabilities Act, specifically Titles II and III.
In some cases, institutions can also face legal action under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 or even state-specific accessibility laws. The point is that non-attention to web accessibility can cost an institution plenty of money and lead to legal suits.
But the good news is that you can avoid these expensive costs by simply running periodic WCAG audits. Here’s what you must know about manual accessibility audits.
The Manual Web Accessibility Audit Process
To give you a short description of what goes into the process of manually auditing a website for accessibility compliance, here’s a brief breakdown of all the key steps:
Determine which pages, features, and content are most critical or representative of your website’s overall accessibility. Then prepare necessary resources such as assistive technologies like screen readers, WCAG accessibility checklists, and browser extensions.
Note: Make sure auditors are familiar with these tools and web accessibility principles.
These are some elements that need to be checked in an accessibility audit:
- Navigation: Keyboard usability and logical order
- Headings: Proper hierarchy and clarity
- Images: Accurate and descriptive alt text
- Multimedia: Captions and transcripts
- Forms: Label associations and error handling
- Color Contrast: Text/background differentiation
- ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) Usage: Correct roles and attributes
After completing the audit, the accessibility audit report should include an executive summary, detailed findings, and visual examples. It should prioritize issues and provide clear remediation steps.
Lastly, you can suggest training for teams to improve future accessibility practices.
Advantages of Manual Accessibility Audits
Some of the benefits of manual accessibility audits are as follows:
- Manual audits allow for a thorough examination of a website’s accessibility. Human testers can identify issues related to context and usability that machines may overlook.
- Testers can assess the practical experience of users with disabilities. Therefore, ensure that interactive elements, content, and navigation are intuitive and functional in real-world scenarios.
- Lastly, manual audits offer a perspective that reflects the experience of users with disabilities by using assistive technologies like screen readers and voice recognition software.
Limitations of Manual Accessibility Audits
There are some disadvantages of the manual audit, including:
- It can be very tiresome, especially when it involves the evaluation of each page and feature. Most educational institutions have websites with multiple web pages and sections.
- Due to the detailed and personalized nature of manual audits, they can be more expensive compared to automated tools.
- Human evaluators may interpret web accessibility guidelines differently, leading to subjective findings. Unless auditors follow a standardized approach, the audit results will be inconsistent.
Automated Tools for Web Accessibility Audits: Advantages and Limitations
Web accessibility audit automation provides a faster and cheaper way to detect surface-level accessibility issues.
Such audits are conducted using software tools that look for known accessibility problems. Tools such as WAVE can quickly find such barriers by comparing them with guidelines such as the WCAG.
Advantages of Automated Web Accessibility Audits
Here are the key benefits of automated web accessibility audits:
- Automated accessibility testing tools follow standardized algorithms, thus ensuring consistent and objective reporting across multiple web pages.
- Ideal for institutions with limited budgets, as these tools often require fewer resources than manual audits.
- These tools allow for continuous or frequent checks and help institutions maintain compliance as content is updated.
Limitations of Automated Web Accessibility Audits
Below are some of the drawbacks of automated web accessibility audits:
- Automated accessibility testing tools often miss more complex issues like usability problems or context-specific barriers that affect user experience.
- These tools can’t simulate real-world interactions for students with disabilities, thus limiting their ability to assess practical usability.
- Automated audits often require a manual follow-up to address deeper or more nuanced accessibility issues, which increases the overall effort.
How to Prioritize Web Accessibility Improvements on a University Budget?
According to research, higher education institutions are offering some accessible course materials, such as braille texts or captioned videos, to students. Additionally, universities are adopting Universal Design for Learning principles in their course development.
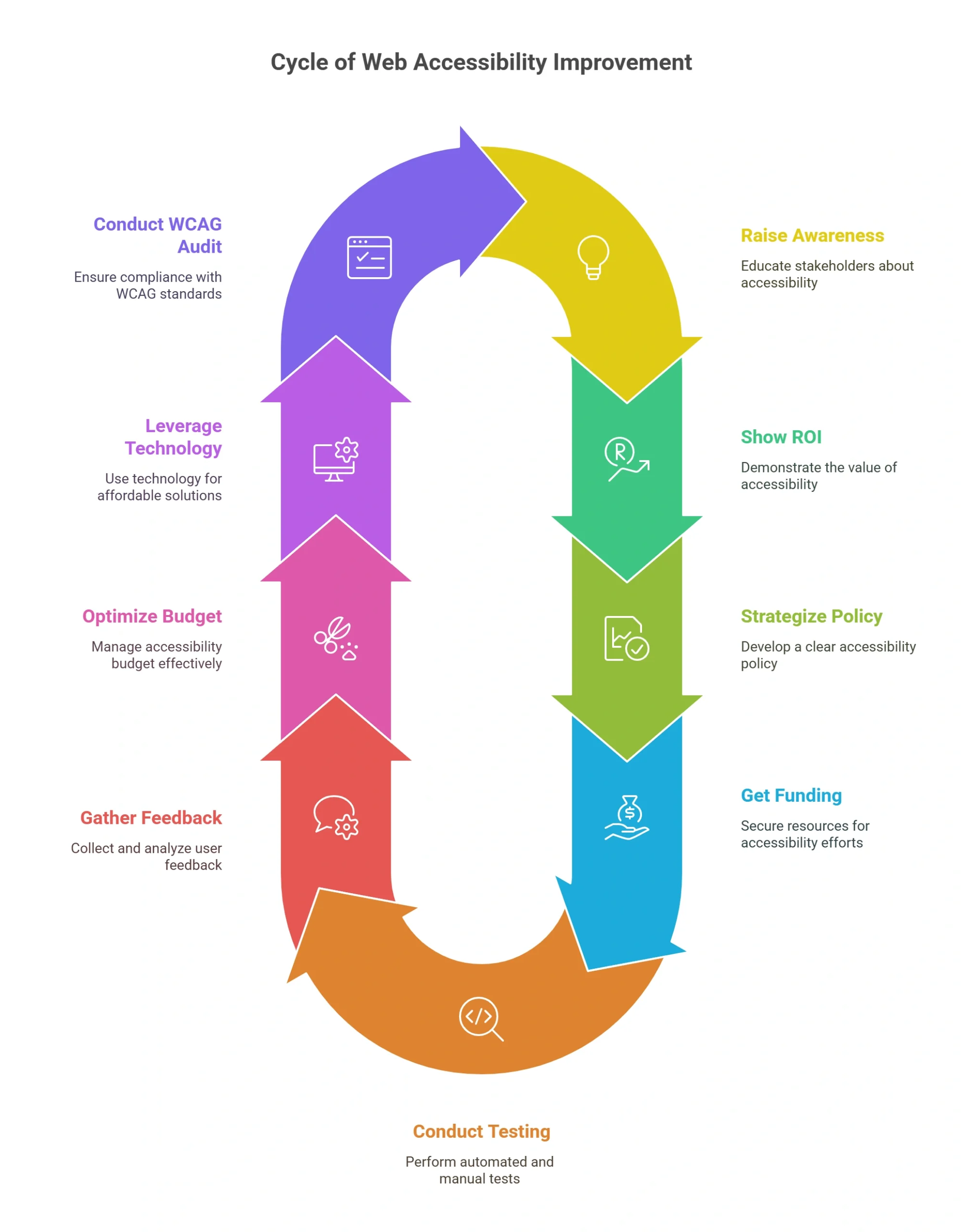
Here are ways to prioritize WCAG accessibility audit reports on a university budget:
1. Raise Awareness
Raising awareness of its importance can garner the most accessibility support. This can be achieved through workshops on education, lunch-and-learn sessions, or even internally sharing informative videos and articles.
Hands-on exercises build empathy and understanding among decision-makers.
2. Show Return on Investment
To seek stakeholder investment in accessibility, benefits need to be tangible and communicated. A strong business case can be made with many of the following:
- Improved Engagement
- Better Understanding
- Legal Consequences
- Improved SEO
- Brand Enhancement
3. Strategize an Accessibility Policy
When an organization commits to accessibility, it’s important to write out that commitment in an accessibility policy. The document should include the institution’s goals, refer to important guidelines like the WCAG, and project a timeline for compliance.
4. Get Funding for Accessibility
Although this may prove challenging in identifying the necessary resources to effect improvements in accessibility, the following are some strategies to consider:
- Early Accessibility Checks: It is much cheaper to identify and fix accessibility issues at the outset of the development phase than it is later.
- Apply for Grants: Several federal grants are available for funding accessibility programs. These may be offered to institutions in certain regions.
- Internally-Generated Grants for Accessibility: This includes shifting funds from other areas within the organization and other external sources such as tax incentives, crowdfunding, or private donations.
5. Conduct Automated and Manual Testing
Leaders must conduct consistent testing to ensure conformance and reduce costly revisions later.
Automated accessibility tests will find common issues. Complete accessibility requires automated testing to be accompanied by manual audits, especially ones conducted by people living with disabilities.
6. Gather and Act on User Feedback
Real user feedback is irreplaceable when refining accessibility. Even a website that is technically compliant with the rules can adopt some points from actual users that may need to be worked on.
Make sure users can provide feedback and a feedback review process to be set up.
7. Make the Most of your Accessibility Budget
When funding is made available, it is important to make the most of an accessibility budget. Here are some options:
- Simplify your content for accessibility
- Go with the vendors recognized for providing quality right from the start, with limited corrections.
- Find opportunities to save using bulk discounts that help stretch the budget further.
8. Leverage Technology for Affordable Accessibility
When budgeting for accessibility, consider solutions that balance high quality and accuracy. A service that consistently delivers solid quality will benefit your organization in time and financial resources over time.
9. Conduct a Comprehensive WCAG Audit
The WCAG audit means scrutinizing all the existing web-based programs for their accessibility. Here are some best practices:
- To make the process even easier, the WCAG 2.0 Web Accessibility Checklist is recommended. Through the use of these checklists, institutions can be assured their accessibility automation tools meet government standards for accessibility.
- Include specific benchmarks and targets within your accessibility policy to help inform your institutional journey.
- Create some friendly competition among departments or campuses that will help motivate everyone toward universal accessibility.
- Provide realistic timelines, such as a timeline for achieving web content screen-reader accessibility in one year and developing accessible media portals in the next.
- Regularly audit progress and accountability of faculty on the need for accessibility practices.
- Incentivize faculties who show a clear commitment to providing accessible materials in their courses, including considering this in tenure processes.
- Make accessibility of course materials a top concern when evaluating instructor-created content.
- Add accessibility questions when students complete course evaluations.
Conclusion
It shouldn’t be surprising that web accessibility in education is not simply desirable but necessary in the growing and heavily tech-based society. It is about fairness, diversity, and making sure that no student is discriminated against or marginalized.
Hurix Digital is your trusted partner in this journey towards accessible education. Our web accessibility consultant combines expertise, cutting-edge technology, and a deep commitment to inclusivity.
Are you willing to share the qualities of your educational content with the masses? Contact us today. Together, let’s help build a fair environment by using digital tools to support students in need of special accommodations.
Summarize with:

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful