How Accessibility Audits Improve Learning Experiences and Boost Student Retention
Summarize with:
In recent years, online education has reshaped the learning landscape, with a growing emphasis on creating accessible learning environments.
Today, there’s a growing demand among learners with disabilities for equal access to all opportunities and resources. The seeds of this trend were sown as early as 1990 when the American Disabilities Act (ADA) was first constituted. The ADA has evolved significantly in the digital economy, including aspects such as web accessibility.
As of 2022, it was reported that over 70 million people in the US live with disabilities. By making all websites accessible, educational institutes can stay relevant, attract new audiences, and enhance enrollments. One of the first steps in this direction is for institutions to conduct a thorough accessibility audit.
This blog explores accessibility audits, their importance within educational establishments, and particulars of how such audits may assist in developing an inclusive culture and improving the quality of education. Dive in!
Table of Contents:
- 4 Key Pillars of an Accessibility Audit
- The Role of Accessibility Audits in Online Education
- 6 Strategies for Conducting an Accessibility Audit
- Top 3 Benefits of an Accessibility Audit
- Long-Term Impact of Inclusive Websites
- In Conclusion
4 Key Pillars of an Accessibility Audit
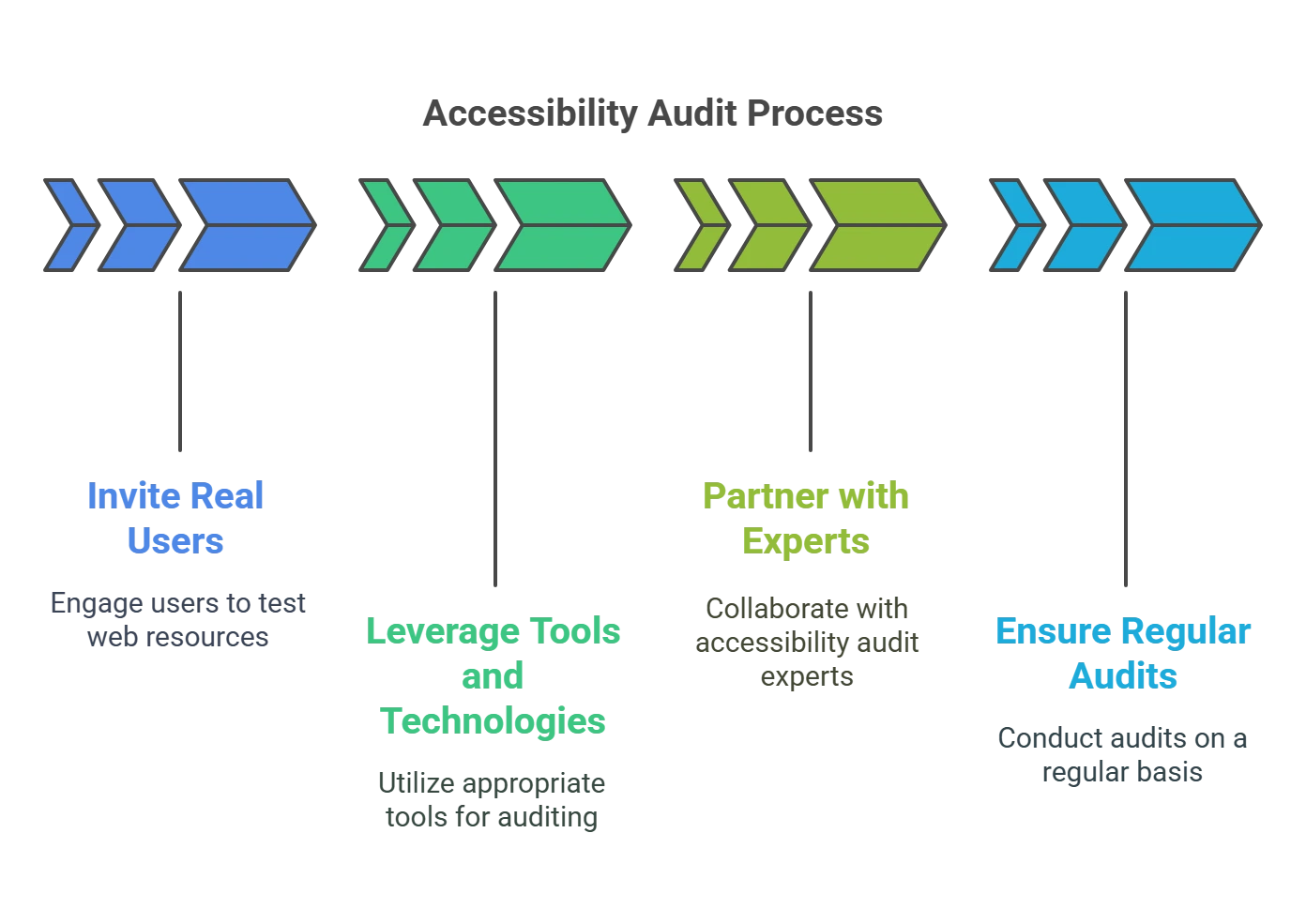
Educators must take several steps to conduct an effective accessibility audit. They are:
Step 1: Invite Real Users to Test All Web Resources
The first step is to consider the feedback of end users of any web resource. Examples of resources may include an educational institute’s admissions website and app, educational material such as eBooks, and digital libraries of on-demand learning resources.
A cross-section of users with diverse disabilities, such as visual, hearing, cognitive, intellectual, and motor challenges, must be invited to participate. Further, ensure the user access review audit report is detailed and data-driven.
Step 2: Leverage the Right Tools and Technologies
Organizations must consider harnessing technology to ensure a comprehensive accessibility audit. Today, a wide range of Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) audit tools, technologies, and accessibility solutions are available.
By leveraging these tools, educators can enhance testing capabilities in terms of speed and effectiveness. They can cover the full spectrum of accessibility features—from captions and speech-to-text capabilities to the lack of alt text.
Step 3: Partner with Accessibility Audit Experts
Accessibility is emerging as a specialized domain, with innovations spearheaded every day. Organizations may not have the in-house expertise to conduct a professional accessibility audit. Working with external experts can help institutions derive a higher Return on Investment (ROI) from their efforts.
Step 4: Ensure Regular Audits
Every piece of new content added to a website or new web properties launched by institutions must be audited for accessibility. Thus, regular ADA website audits must become a part of the organization’s culture and process.
The Role of Accessibility Audits in Online Education
Today, there’s a growing focus on improving educational access for people with disabilities. Public policies have evolved to ensure people with disabilities can access all digital products and services.
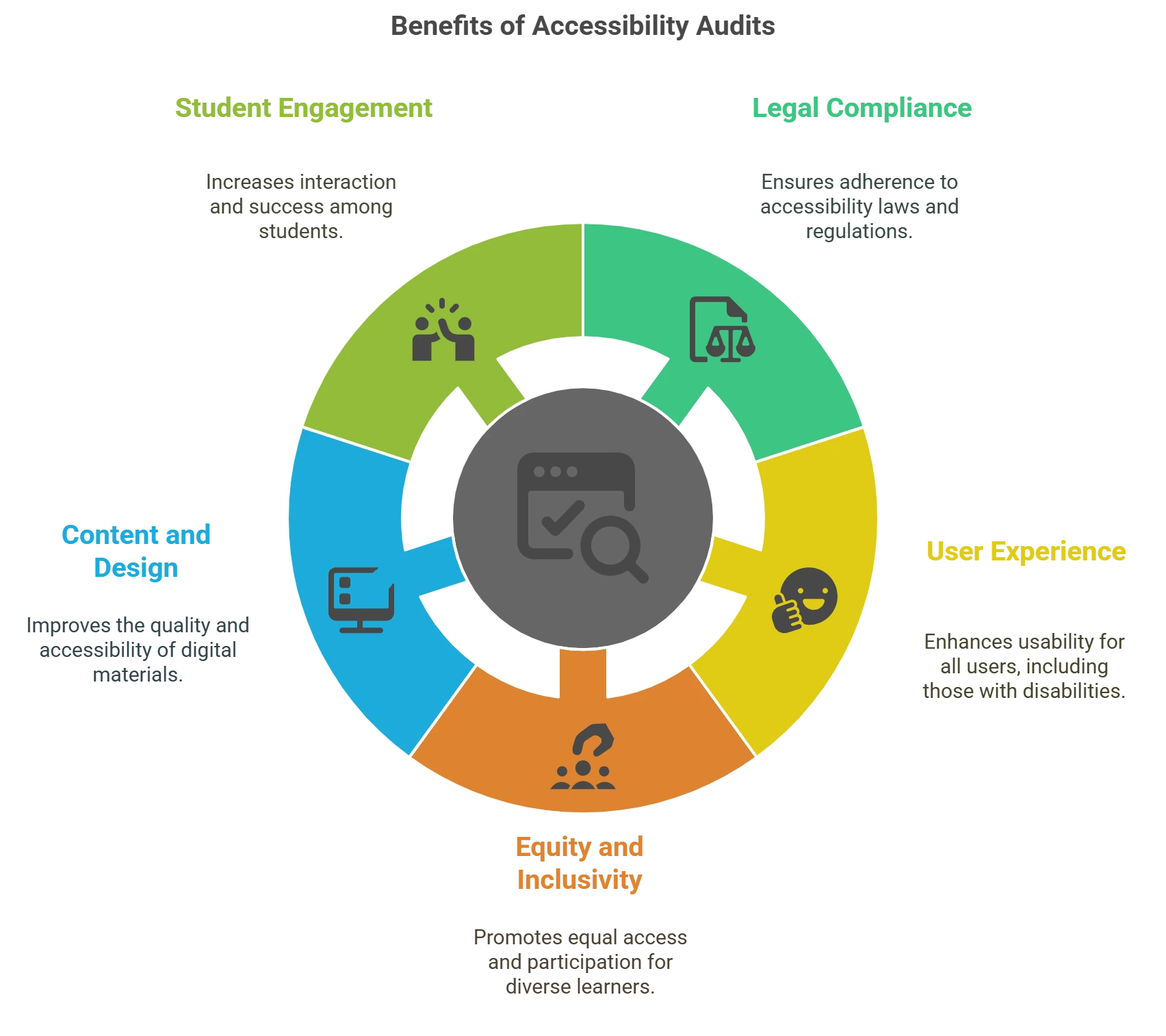
Here’s a snapshot of the key roles of accessibility audits in online education:
1. Ensuring Legal Compliance
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) are enforced in several areas. By identifying compliance gaps, accessibility audits assist educational institutions in ensuring that their digital platforms meet these criteria and stay out of trouble with the law.
2. Improving User Experience
Audits draw attention to accessibility issues such as difficult navigation, untagged photos, or inaccessible multimedia that negatively impact the user experience for students with disabilities. By tackling these problems, institutions establish an inclusive atmosphere where all students can engage in and navigate the learning process equitably.
3. Promoting Equity and Inclusivity
By empowering educational platforms to promote equity, accessibility audits guarantee that students with disabilities have equal access to educational opportunities as their peers. Teachers can encourage diversity in their learning environment and support a varied student body by producing accessible content.
4. Enhancing Digital Content and Platform Design
Through accessibility audits, online education providers can assess the usability of digital content, such as textbooks, quizzes, and discussion boards. Improvements in platform design, like adding alternative text for images or ensuring keyboard navigability, enhance the overall accessibility of learning materials.
5. Increasing Student Engagement and Success
Accessible platforms allow students with disabilities to engage more effectively with course content, increasing participation and academic success. Students who can navigate a platform independently are more likely to stay engaged and motivated throughout their educational journey.
6 Strategies for Conducting an Accessibility Audit
Conducting an accessibility audit requires a well-thought-out approach to ensure that educational platforms are inclusive, compliant, and user-friendly.
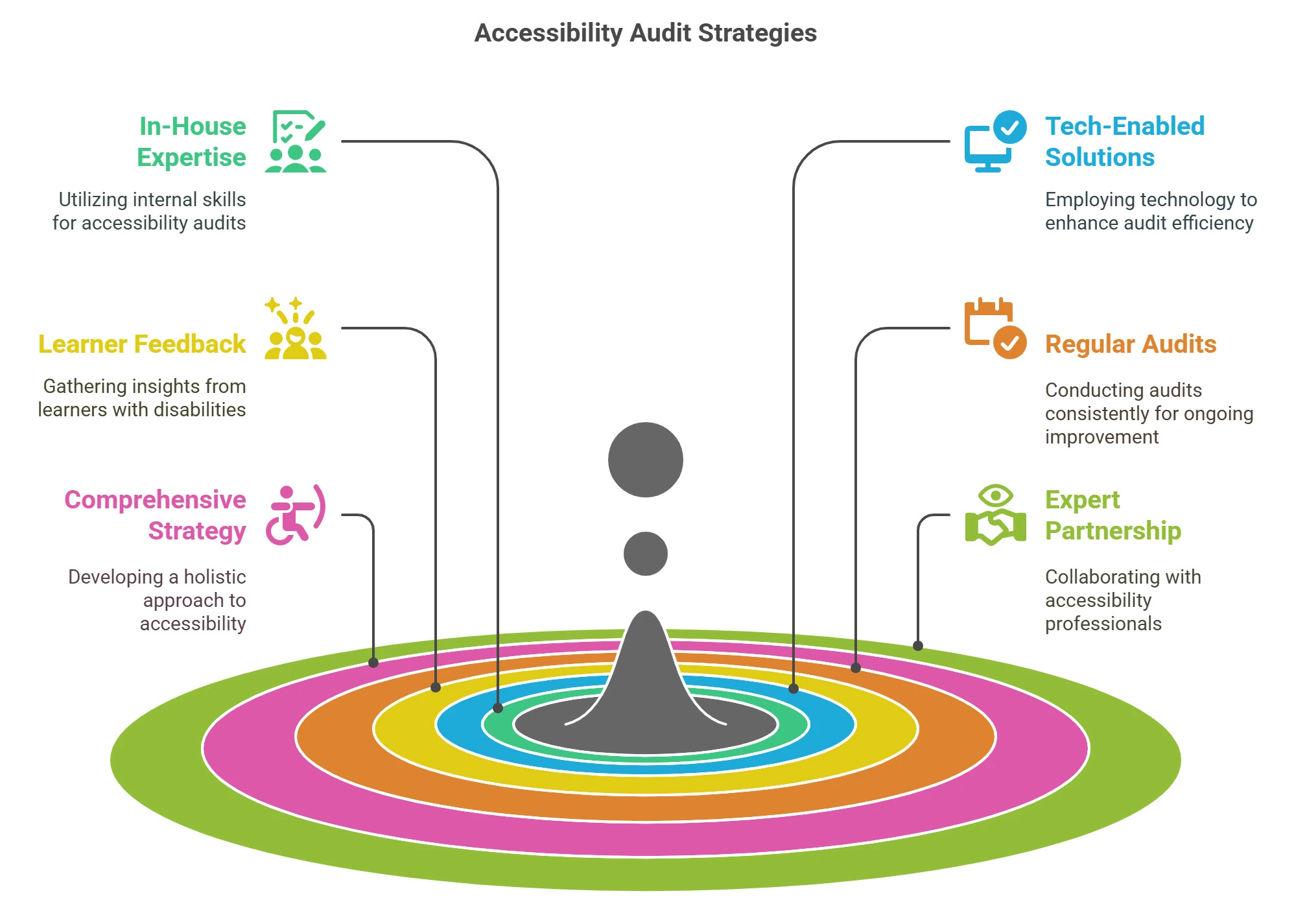
Here are some strategies to effectively conduct an accessibility audit:
1. Access to In-House Expertise and Capacity
Educational organizations may have in-house teams comprising instruction designers, web developers, and technology professionals who develop, publish, and manage digital assets.
However, an effective and high-impact shift towards more inclusive environments demands specialized accessibility expertise. Organizations must carefully assess whether they can execute such a transition in-house.
2. Harness Tech-Enabled Solutions
Today, organizations have access to a wide range of Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) tools and technologies that can help them boost their web accessibility audit capabilities.
Educators can test for the full spectrum of accessibility features missing from their digital resources by running an audit on their websites. These range from closed captions and ALT text to read-aloud, video voiceovers and customizable text sizes. For instance, a superior tool can help educators assess a web page for accessibility quickly and effectively using a rules engine.
3. Invite Feedback from Real Learners with Disabilities
Educators must have an in-depth understanding of the barriers faced by learners with disabilities. They must also understand their needs and aspirations.
One of the most valuable ways to do so is to invite real learners with disabilities and learning challenges to use all digital assets. Educators can chronicle detailed feedback on their experience and turn these inputs into solutions.
4. Conduct Audits Regularly
Today, conducting regular accessibility audits is considered a best practice. Accessibility guidelines, solutions, and users’ needs are continuously evolving. Hence, educators need to stay current with compliance, technological advances, and their understanding of learner needs. Conducting audits at regular intervals helps them stay current.
5. Build a Comprehensive Accessibility Strategy
Conducting an accessibility audit is not enough. This activity is just the beginning of a larger journey.
- Educators must develop a comprehensive strategy for upgrading all their digital resources. By doing so, they will be able to attract new learners into their ecosystem, build a diverse cohort of students, and ensure WCAG compliance across the board.
- Educators must also consider training their teaching facilitators, instruction designers, and content creators to nurture a sensitive learning culture and a deeper understanding of how to create and publish quality learning resources for people with disabilities. They must be aware of auditing tools and the accessibility features available to curate an inclusive ecosystem.
6. Consider Partnering with an Accessibility Expert
If organizations do not have the capacity to tackle accessibility in-house, they can consider outsourcing this important function to an expert.
A superior accessibility expert comes with an extensive understanding of the barriers faced by people with disabilities, the skills and knowledge, and the best accessibility solutions to execute a thorough audit.
Furthermore, they must be able to enable the entire transition to an accessible digital ecosystem.
Top 3 Benefits of an Accessibility Audit
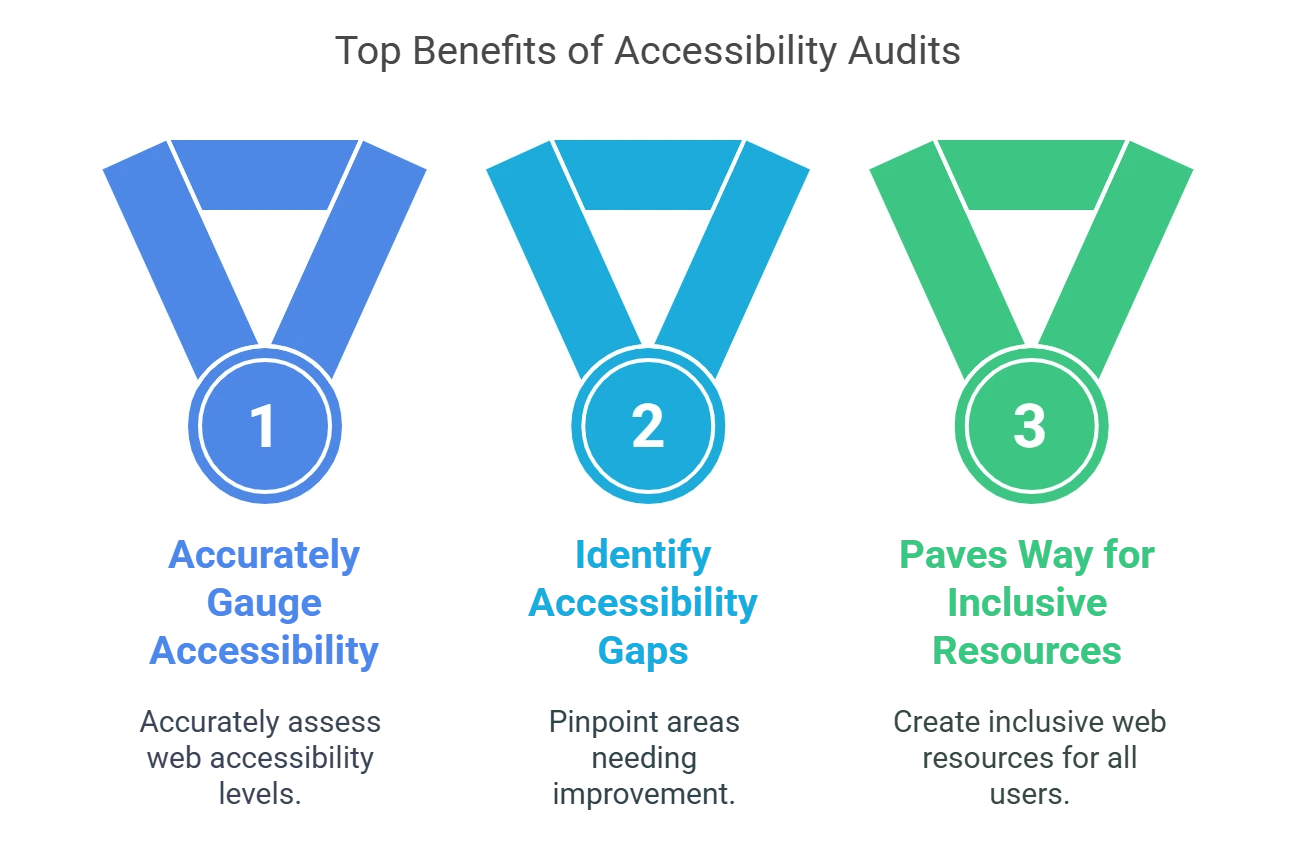

Regular accessibility audits can help educators in multiple ways, including:
1. Accurately Gauge the Level of Web Accessibility
Educators can establish the status of web accessibility across all their digital assets. They can get a realistic picture of the work needed to make their digital footprint accessible to the learners.
2. Identify Accessibility Gaps
A comprehensive accessibility audit helps educators identify the key gaps that must be addressed. However, they must ensure that the audit addresses challenges across the entire spectrum of disabilities.
3. Paves the Way for Inclusive Web Resources
The ultimate aim of an ADA compliance audit is to ensure that all web resources are accessible to the end users. However, such a review lays the foundation for this transition. Using the audit’s findings, accessibility experts can build a strategic road map to address the gaps using strategy and technology.
Long-Term Impact of Inclusive Websites
Educational institutes must understand the advantages of an inclusive approach toward all their digital assets, such as inclusive websites. This will help in the following:
1. Accessible to Learners with Disabilities/ Challenges
Learners with disabilities can fully access content on websites ranging from admissions pages to digital resources. For instance, say learners with visual challenges visit the admissions website; they can navigate the entire website easily due to its accessibility features.
2. Helps Boost Enrollment Rates
Accessible websites reduce barriers and open up opportunities for learners with disabilities. A comprehensively accessible website can boost enrollment by students with a spectrum of disabilities, from physical and cognitive to motor disabilities.
Thus, inclusive websites give educational institutions a competitive edge. They create a positive impression and can lead to a higher enrollment rate.
3. Boosts Learning Effectiveness
Ensuring learners access all-inclusive websites helps boost engagement, knowledge absorption, and retention. They can learn quickly, improve their test scores, and build the knowledge and skills required for future opportunities in the world of work.
In Conclusion
Offering learners an accessible learning environment is fast becoming a non-negotiable aspect of online learning. Educators looking to build a sustainable model must consider making the shift quickly and impactfully.
The first step is to conduct an accessibility audit of all digital assets. Based on the findings, they can fill the gaps and leverage technology to elevate learning to the next level.
Conducting an accessibility audit is important for educational institutions looking to transform into inclusive organizations. This process paves the way for educators to build inclusive resources relevant to a wider audience and address the challenges of existing students.
The best approach is for organizations to partner with a technology specialist with expertise in accessibility transformation. These early investments translate to higher student enrollment and retention rates and greater learning effectiveness.
If your organization seeks to conduct accessibility audits and transition into an inclusive organization, technology will play an important role in this process. Hurix Digital has expertise in building accessible ecosystems in education and beyond.
Get in touch with us to start a conversation.
Summarize with:

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful