
Is Your Website Vulnerable to Cyber Attacks? What You Can Do About It?
Cyber security or IT security protects computer systems and networks from information disclosure, theft, damage to hardware and software, and disruption of services. The goal? Eliminate risks from cyber-attacks and guard systems, networks, data, and devices from unauthorized exploitation.
Did you know the average website faces 94 attacks every single day? These attacks can expose customer information, harm your brand reputation, and potentially cause serious financial damage. The good news is that website security doesn’t have to be overwhelmingly complex.
Table of Contents:
- Legal Requirement for Cyber Security
- Why Does Cyber Security Matter?
- The Real-World Impact of Security Breaches
- Common Types of Cyber-Attacks
- Penetration Testing: Your Security Shield
- Penetration Testing Stages
- When to Conduct Penetration Testing
- Cyber Security Tools and Services
- Best Practices for Website Security
- Cyber Security at Hurix Digital – Best Practices
- Partnering for Proactive Website Security
- Conclusion
Legal Requirement for Cyber Security
Yes, having cyber security measures is crucial for any organization. The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and DPA (Data Protection Act) 2018 require organizations to implement appropriate security measures to protect personal data. Depending on your industry and the type of data you collect, you might face strict compliance requirements that could result in hefty fines if breached.
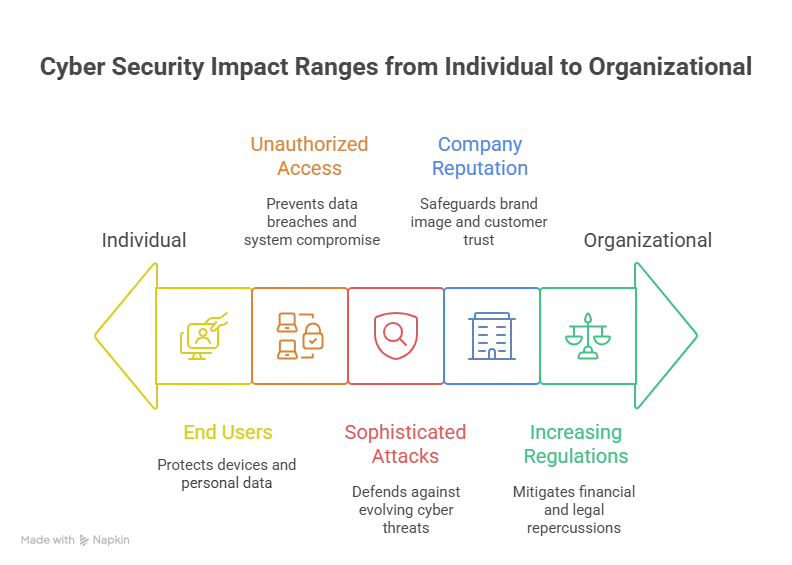
Why Does Cyber Security Matter?
Your website serves as more than a virtual pamphlet. It plays a crucial role in shaping your brand image and can serve as an entry point to valuable user information. Here’s why cyber security deserves your immediate attention:
- Increasingly sophisticated cyber-attacks are emerging: The tactics and reach of cyber attackers continue to expand, including malware and ransomware, phishing, social engineering, insider threats, advanced persistent threats, and more.
- Unauthorized user access must be prevented: Cyber security addresses system and network vulnerabilities, securing them from unauthorized access.
- End users and devices get protected: Data privacy is maintained through proper cyber security practices. Network protection is ensured.
- Regulations are increasing the costs of cyber security breaches: Privacy laws like GDPR and DPA impose hefty fines on organizations that ignore cyber attack threats.
- Company reputation at stake: Strong cyber security measures translate into improved trust with your clientele and stakeholders.
The Real-World Impact of Security Breaches
When targeted by cyber threats, the aftermath can be severe:
- Data Breaches: Hackers can steal sensitive information like customer data, financial details, or login credentials. This results in identity theft, financial losses, and reputational damage that can last for years.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software can infect your website, redirect users to harmful sites, steal data, or disrupt website functionality. This damages user trust and negatively impacts search engine rankings.
- Downtime and Disruption: Website attacks can render your site inaccessible to users, causing lost revenue and frustrating potential customers. Imagine an e-commerce store experiencing website downtime during peak shopping season; the impact is detrimental.
- Compliance Issues: A breach in website security can result in breaking data privacy regulations, leading to fines and reputation damage.
Recent research revealed that 93% of organizations have faced data breaches in the form of identity theft two or more times in the past year. This highlights how critical proactive security measures have become.

Common Types of Cyber-Attacks
Cyber security risks become even more challenging when organizations resort to remote working, giving less control over employee activities and device security. A cyber attack can cost organizations billions and severely damage reputation. Organizations will likely lose sensitive data and face huge fines.
Here are the different types of cyber-attacks you need to watch for:
- Malware: A kind of malicious software that can use any file or program to harm computer users, such as worms, viruses, Trojans, and spyware.
- Social Engineering: Users are tricked into breaking security procedures, allowing attackers to gain sensitive, protected information.
- Phishing: Fraudulent emails and text messages resembling those from reputable sources are sent at random to steal sensitive information such as credit cards.
- Spear Phishing: A form of phishing attack with a particular (intended) target user or organization.
- Ransomware: Another type of malware where the system is locked by an attacker through encryption that won’t decrypt until the ransom is paid.
Other common attacks include insider threats, distributed denial of service, advanced persistent threats, man-in-the-middle attacks, botnets, vishing, business email compromise, SQL injection attacks, and zero-day exploits. Effective training enables employees to understand the significance of cyber security.
Penetration Testing: Your Security Shield
Penetration testing (ethical hacking) is the deliberate launching of simulated cyber-attacks to spot vulnerabilities that can be exploited in systems, websites, networks, and applications. The main objective? Identify security inadequacies, flaws, and weaknesses before real attackers do.
Penetration tests expose all kinds of vulnerabilities that would let attackers access the system, enabling companies to tighten their security policies. These tests collect details about possible targets, spot potential entry points, and attempt to break in.
Where web application security is concerned, penetration testing improves a web application firewall (WAF). Testers attempt to breach application systems, including application protocol interfaces (APIs), frontend servers, and backend servers to uncover vulnerabilities vulnerable to code injection attacks. Penetration tests help fine-tune WAF security policies and patch detected vulnerabilities.
Penetration Testing Stages
- Planning and reconnaissance: The scope and goals of the test are defined, including which systems to address and testing methods to use. Network names, domain names, and mail servers are collected to understand how a target works and identify weaknesses.
- Scanning: Understanding how the target application responds to various intrusion attempts using static analysis and dynamic analysis. Static analysis inspects an application’s code to estimate behavior while running. The tool scans the entire code in a single pass. Dynamic analysis inspects the application’s code in a running state, providing a real-time view into an application’s performance, making it more practical.
- Gaining Access: The target’s vulnerabilities are uncovered using web application attacks, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and backdoors. Testers exploit these vulnerabilities by stealing data, escalating privileges, and intercepting traffic to understand the damage they can cause.
- Maintaining access: Advanced persistent threats often remain in a system for months to steal sensitive data. This stage aims to see if any vulnerabilities can achieve a persistent presence in the exploited system.
- Analysis: Pen test results are compiled into a report detailing vulnerabilities that were exploited, sensitive data accessed, and how long the pen tester remained in the system undetected.
Security personnel analyze this information and configure the company’s WAF settings and application security solutions to patch vulnerabilities and protect against future attacks.
When to Conduct Penetration Testing
Companies should commission security testing annually, with additional assessments after any significant infrastructure changes, before product launches, and during mergers and acquisitions. Companies with very large IT estates, processing large volumes of personal and financial data, or with strict compliance requirements should conduct pen tests more frequently.
Penetration testing satisfies compliance requirements for security auditing procedures, PCI DSS and SOC 2, among others. While certain standards, such as PCI-DSS 6.6, can be satisfied through the use of a certified WAF, penetration testing remains appealing and useful for comprehensive security.
Cyber Security Tools and Services
Cyber security vendors offer a variety of security tools and services:
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Firewalls
- Endpoint protection
- Antimalware
- Intrusion prevention/detection systems (IPS/IDS)
- Data loss prevention (DLP)
- Endpoint detection and response
- Security information and event management (SIEM)
- Encryption tools
- Vulnerability scanners
- Virtual private networks (VPNs)
- Cloud workload protection platform (CWPP)
- Cloud access security broker (CASB)
Career opportunities in cyber security include Chief Information Security Officer, Chief security officer, security engineers, security analysts, security architects, penetration testers (ethical hackers), data protection officers, cryptographers, and threat hunters.
Best Practices for Website Security
Security is something you can never just set up once and forget about. Here’s a comprehensive cyber security checklist covering both development and maintenance:
- Follow Secure Coding Principles: Following secure coding principles lowers the chances of vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting attacks. These principles involve data validation, input management, and using trusted libraries and frameworks with built-in security features.
- Implement Strong Authentication: Cyber attackers target login sections, making strong authentication crucial. Set password requirements that include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Ensure Secure Server Configuration: Where your website is hosted plays a role in its security. Configure web servers securely by using firewalls to filter traffic, regularly updating server software with security fixes, and disabling unnecessary services that malicious actors could exploit.
- Conduct Vulnerability Assessments: Code can have vulnerabilities. Regular vulnerability assessments identify and address weaknesses in your website’s code, configurations, and third-party plugins.
Cyber Security at Hurix Digital – Best Practices
A recent study showed that cyber attacks happen every 39 seconds, with most targeted toward web applications. Here are some best practices followed at Hurix Digital for protecting web applications against common attacks:
- Input validation: Checking user-submitted variables for malicious or erroneous input that can cause strange behavior. Implement a whitelist containing patterns or criteria that match benign input. The whitelist approach allows conditions to be met and blocks everything else.
- Single Sign-on and Multi-Factor Authentication: While single sign-on authentication is convenient, pulling user credentials from a directory or identity database service, multifactor authentication makes your application more secure by adding additional authentication steps.
- Application errors: One should never reveal sensitive application implementation or configuration settings, as this can be exploited by attackers. Keep error messages generic. Never store secrets in plain-text passwords.
- Code reviews: During development and testing stages should always be done to provide code coverage and ensure secure code practices are utilized. Application scanning helps identify vulnerabilities prior to deployment.
- Protection from malicious attacks: Implement input validations, anti-forgery tokens, cross-site scripting attack prevention, brute force attack prevention, checking sensitive information disclosure, and other strong coding practices.
- Authentication and session management: Address vulnerabilities resulting, potentially, in user impersonation, protection, and credential strength.
- Authorization: Test the application’s ability to protect against vertical and horizontal privilege escalations.
- Malware protection: Don’t expose internal hardware configuration details as much as possible in the web app, and use known modules used worldwide.
- Port scanning prevention: Keep unused ports closed with restricted access so hackers can’t easily exploit them.
- Denial of service attack prevention: Don’t allow continuous hits to specific APIs (Application Programming Interface) that are sensitive in terms of vulnerabilities or functionalities of the web application.
OWASP Top 10 Security Vulnerabilities Testing at HURIX
The Hurix testing team performs testing that addresses vulnerabilities deemed the most common web application security risks by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP). By addressing these risks and writing appropriate code with robust tests, developers can create secure web applications, keeping confidential data safe from hackers:
- Broken authentication
- Sensitive Data Exposure or Information Disclosure
- SQL Injection
- Broken Access Control
- Cross Site Scripting
- Insufficient Time Outs
- Insecure Deserialization
- Insufficient Logging and Monitoring
- Link Manipulation
- Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
Partnering for Proactive Website Security
While website security is a shared responsibility, partnering with a website security expert can provide an extra layer of protection. Here are comprehensive website security services worth considering:
- Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Identify and address vulnerabilities before hackers exploit them
- Website Monitoring and Threat Detection: Proactively monitor your website for suspicious activity and take immediate action if needed
- Incident Response Planning and Management: Develop a plan to respond to security incidents efficiently and minimize damage
Conclusion
Making sure your website is secure isn’t a choice—it’s a requirement. By following the methods for development and continuous upkeep, you can greatly minimize the chances of cyberattacks.
A pen test is a form of ethical cyber security assessment undertaken to spot and exploit (safely) vulnerabilities present on a company’s on-premises and remote IT environments. At Hurix Digital, penetration testing engineers scan vulnerabilities within your systems and provide information on potential vulnerabilities. Our experts carry out tests to find weaknesses in the design of your IT infrastructure and assess the extent to which an attacker could gain access to your data.
Keeping your website secure requires continuous effort. Security checks and penetration testing help discover and fix vulnerabilities before they’re exploited. Our skilled website security professionals offer a range of services, including monitoring to detect and respond to security risks promptly, helping you develop action plans to minimize the impact of security breaches.
Whether you’re starting from scratch, going through upgrades, or making unexpected changes, let us be your security expert. Contact us to get started building a secure and resilient online presence.
To know more about cyber security and penetration testing solutions from Hurix Digital, schedule a free call here.

Vice President & SBU Head –
Delivery at Hurix Technology, based in Mumbai. With extensive experience leading delivery and technology teams, he excels at scaling operations, optimizing workflows, and ensuring top-tier service quality. Ravi drives cross-functional collaboration to deliver robust digital learning solutions and client satisfaction
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 
