
Why Accessibility Compliance is Everyone’s Responsibility?
Summarize with:
Despite the importance of accessibility compliance, many businesses have overlooked it for far too long. As a result, their websites and applications may unintentionally exclude individuals with disabilities from accessing their products and services.
However, ensuring accessibility compliance is not solely the responsibility of developers or users; it’s a shared effort among businesses, developers, and users.
Research suggests that in the United States, nearly 98% of web pages remain inaccessible to people with disabilities from a legal perspective. The latest data from the WebAIM Million reveals that in 2023, over 95% of these pages still struggle with WCAG 2 accessibility compliance issues. The increasing complexity of web pages in recent years has added to the challenge.
This oversight poses significant business risks, including potential legal liabilities, reputational damage, and missed opportunities for reaching a broader customer base.
In this post, explore why accessibility compliance is crucial for businesses, the potential risks of non-compliance, and steps that businesses can take to improve accessibility on their websites and applications. Read on!
Table of Contents:
- What Does WCAG Compliance Refer To?
- What is Section 508 Compliance?
- Digital Accessibility Laws in the European Union, the United States, and Canada
- How Can Businesses Be More Accessible in 2025 and Beyond?
- Emerging Technologies and Their Impact of Digital Accessibility
- To Wrap Up
What Does WCAG Compliance Refer To?
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are a set of internationally recognized standards developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). WCAG provides guidelines and a framework for web developers, designers, and content creators to make their websites and online content usable by everyone, including those with disabilities.
The four main principles of WCAG are perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust (POUR). Under these principles, specific guidelines address various aspects of web and mobile application accessibility, such as providing alternative text for images, ensuring keyboard accessibility, and ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies.
Each guideline is assigned a conformance level (A, AA, or AAA), indicating the degree of accessibility achieved.
|
Represents minimum level of accessibility |
|
Mid-level addresses the most common barriers encountered by disabled people |
|
Highest level of accessibility, addressing niche accessibility issues |
WCAG compliance is a must for ethical, legal, and business considerations. Many countries, including the United States, have laws and regulations mandating web accessibility. Non-compliance with accessibility guidelines can result in legal liabilities and reputational damage.
This not only ensures that websites are accessible to people with disabilities but also improves the overall user experience for all users, as it encourages better design practices and usability. Additionally, it opens up businesses and services to a wider audience, potentially increasing customer reach and satisfaction.
What is Section 508 Compliance?
Section 508 compliance means adhering to the standards outlined in Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973.
This act mandates that federal agencies in the United States make their electronic and information technology (EIT) accessible to people with disabilities. This includes websites, software, hardware, and other digital tools these agencies use.
Section 508 specifically applies to federal agencies, but its principles and guidelines are often adopted voluntarily by other organizations and businesses that want to make their digital assets accessible to everyone.
Compliance with Section 508 is a legal requirement for federal agencies today. It also serves as a benchmark for accessibility in the wider context of web development and digital content creation.
Digital Accessibility Laws in the European Union, the United States, and Canada
In the European Union, efforts to assimilate the requirements for accessibility in online spaces have materialized in the form of the European Accessibility Act. Proposed in 2011 and enacted in 2019, this Act aims to create consistency in accessibility standards applicable to both public and private sectors.
The enforcement of these standards will become mandatory as of June 28, 2025, reflecting the EU’s commitment to fostering an inclusive digital environment. Similarly, in the United States, the digital accessibility industry has been experiencing gradual but notable developments. The most significant update came in 2022 when the United States Department of Justice clarified that the Americans with Disabilities Act applies to web content also.
On August 4, 2023, the U.S. DOJ issued the eagerly awaited notice of proposed rulemaking (NPRM) outlining accessibility standards for websites and mobile applications covered by Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
Lastly, in Canada, agencies under the federal government are obligated to meet the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.0 AA standard. This has been mandated through Canada’s Standard on Web Accessibility, which has existed since 2011.
The Accessibility Standards Canada’s 2023-2024 plan drafted standards on information and communication technologies, agreeing with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines and reflecting the country’s commitment to digital accessibility.
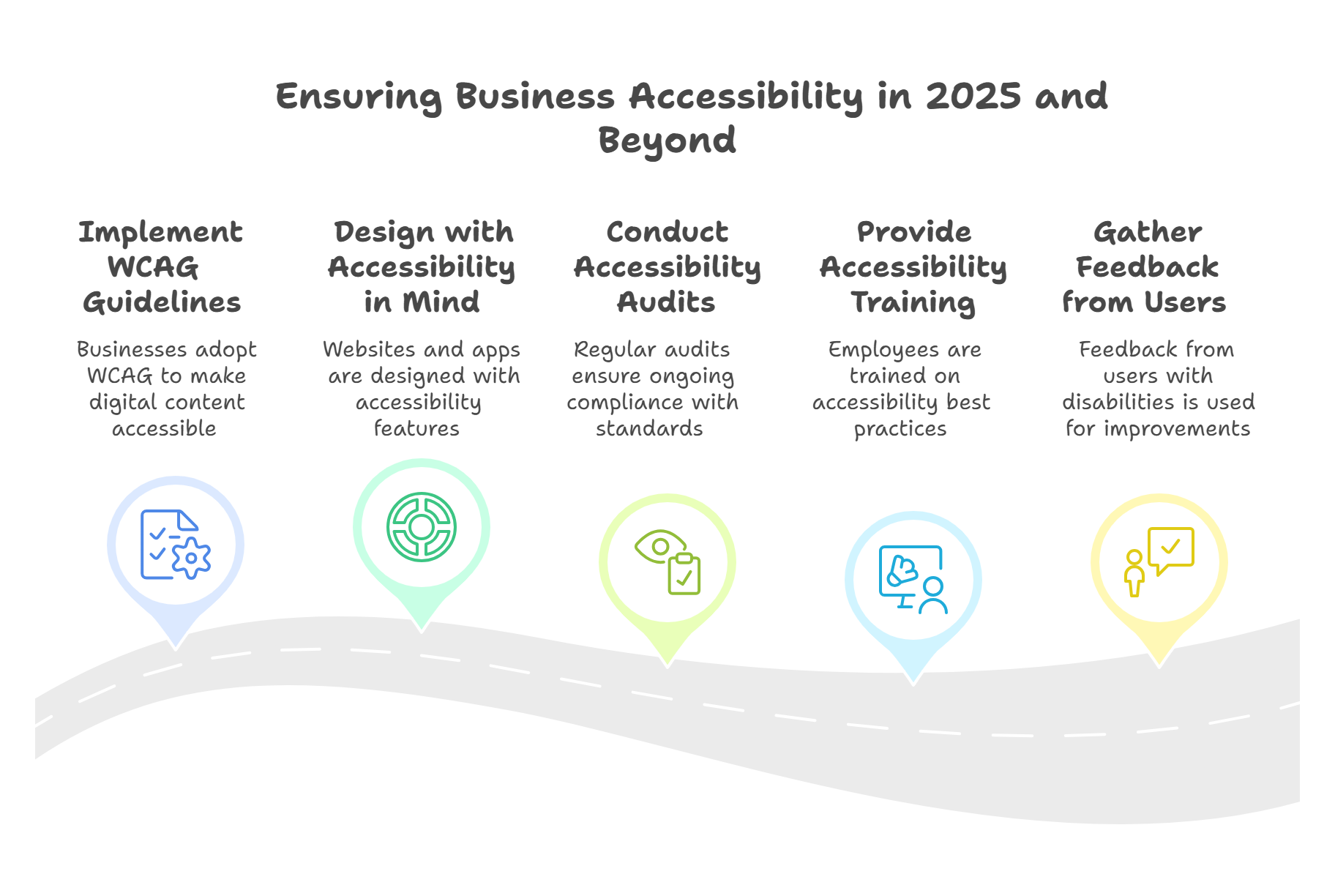
How Can Businesses Be More Accessible in 2025 and Beyond?
Businesses across the globe can take several steps to ensure they comply with accessibility guidelines.
Here’s what they can do:
Step 1: Follow Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
The first step that businesses must take to ensure accessibility compliance is to implement WCAG guidelines. This would automatically make their website, application, and/or digital content accessible to people with disabilities.
Some of the WCAG guidelines include provisions for providing alternative text for images, ensuring keyboard accessibility, and making content perceivable, operable, and understandable.
Step 2: Design Your Website or Application with Accessibility in Mind
When your website or mobile application is still in the design phase, you should adhere to app and website accessibility guidelines. This includes using high-contrast colors, providing clear and consistent navigation, and making interactive elements easily identifiable.
As a business, you must also provide alternative content formats for people with visual or hearing disabilities. You can add audio descriptions for images and text transcripts for videos on your website or in your application.
Step 3: Conduct Periodic Accessibility Audits
Web accessibility guidelines are evolving, with different versions of WCAG, such as WCAG 2.0, 2.1, and the latest iteration, WCAG 2.2. To continue being compliant with these guidelines, you must regularly conduct accessibility audits of your website and digital assets.
Accessibility testing would also help you identify and address any accessibility barriers and would ultimately certify accessibility compliance with the latest digital accessibility standards.
Step 4: Provide Accessibility Training to Your Employees
Businesses must provide accessibility training and education to employees who are involved in creating and maintaining digital content on accessibility best practices and the importance of digital inclusivity.
Raising awareness about the importance of digital accessibility within your organization will encourage a culture of accessibility and inclusion at all levels of your business.
Lastly, businesses must get feedback from people with disabilities to understand their challenges when interacting with your digital platforms. You can use this feedback to improve your platform.
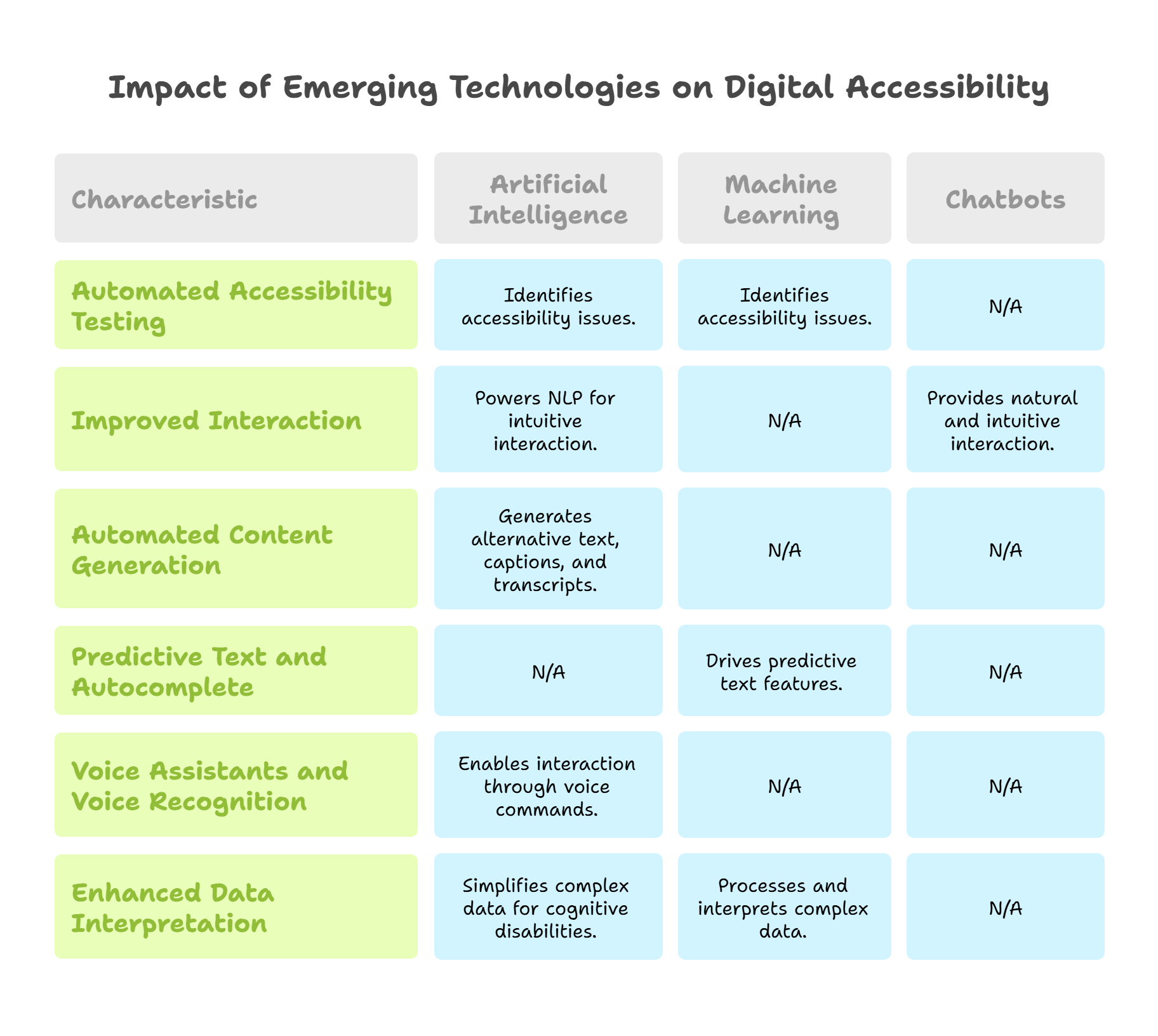
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact of Digital Accessibility
Emerging accessibility technologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and chatbots, have the potential to impact the future of online accessibility in various ways significantly:
1. Automated Accessibility Testing
AI and ML can be employed to automate the testing of digital content for accessibility. These technologies can analyze web pages, applications, and documents to identify potential accessibility issues, simplifying the testing process and ensuring quicker identification and resolution of problems.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Improved Interaction
Chatbots, powered by NLP and AI, can enhance accessibility by providing a more natural and intuitive way for users to interact with digital platforms. This benefits individuals with varying abilities, including those who may face challenges with traditional user interfaces.
3. Automated Content Generation
AI technologies can automate the generation of alternative text for images, video captions, and audio transcripts, improving accessibility for users who rely on screen readers or other assistive technologies.
4. Predictive Text and Autocomplete
Predictive text features, driven by ML algorithms, can assist users with cognitive or motor impairments by reducing the amount of typing required. Autocomplete suggestions based on user input can enhance efficiency and accessibility.
5. Voice Assistants and Voice Recognition
AI-driven voice assistants and speech recognition technologies contribute to accessibility by allowing users to interact with devices and applications through voice commands. This is highly beneficial for individuals with mobility or dexterity challenges.
6. Enhanced Data Interpretation
ML algorithms can help process and interpret complex data, making information more accessible through simplified visualizations or alternative formats for users with cognitive disabilities.
Furthermore, when integrated into digital accessibility tools, it can learn from user interactions and feedback, leading to continuous improvements in providing more accurate and effective accessibility support.
Despite AI and ML’s positive impact, it’s essential to approach the integration of these technologies with mindfulness toward potential challenges and unintended consequences. Ensuring that these technologies are designed with accessibility principles in mind from the outset is very important for creating a digital world that is truly inclusive and accessible to all users.
To Wrap Up
In the pursuit of a digitally inclusive future, there’s a growing recognition of the need for a more intentional approach to digital accessibility tools and technology.
While progress has been made in implementing these solutions, moving beyond mere adoption and focusing on thoughtful utilization is crucial. By understanding the nuanced requirements of diverse users, organizations can enhance the effectiveness of accessibility tools and technology, creating truly inclusive digital environments.
If you need help making your websites and apps easy for everyone to use? Hurix Digital is here to help. Our team of experts can lead your organization in adhering to accessibility guidelines, ensuring that your digital products are accessible to a wide audience.
Contact us to learn more!
Summarize with:

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 




